| BABYLON AND ASSYRIA Ancient
Mesopotamia Later Peoples - Babylon and Assyria :
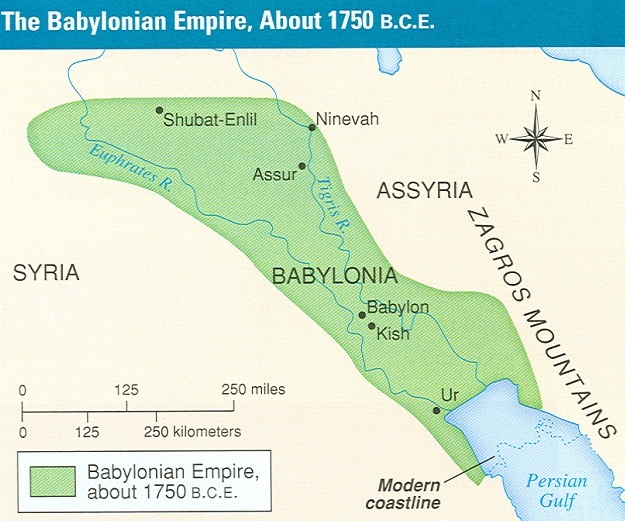
The Babylonian Empire. Notice the location of Babylon, where the Tigris and Euphrates rivers run close to one another. You can see that the city-state of Ur is now under control of the Babylonians. The Zagros Mountains are where the ancient Mesopotamians believed their gods lived.
Hammurabi is best known for a set of laws he gave to his empire known as the Code of Hammurabi. The laws were carved on 8 foot stones, called steles, and placed in the cities of his empire. In this way the laws could not be changed and were posted for all to see, though few people could read. Hammurabi wanted to be known as a fair and just ruler.
You can read some of the laws from the Code of Hammurabi, which I found listed online; what do you think about these laws?
Here is a replica of one of the Steles discovered with the Code of Hammurabi, it is meant to resemble an index finger. The fingernail shows Hammurabi standing, receiving the laws from the seated sun-god, Shamash. The laws are written below the figures in cuneiform using the Akkadian language.
After the reign of Hammurabi, the Babylonians were attacked and weakened by the Hittites, a group of people from Asia Minor. The capital city of Babylon was sacked. Eventually, the Assyrians would conquer Babylon and Mesopotamia, but the lasting achievements of Babylon included advances in mathematics, astronomy and trade.
Ancient Assyria and the Assyrians :
This is the Taylor Prism, named after the archaeologist who discovered it in 1830. The prism a six-sided clay object with a paragraph of cuneiform on each side. The language is Akkadian. Sennacherb, king of Assyria from 704-681 BC, had this made. On the prism, Sennacherib brags about his military conquests, including the siege of the Judean city of Lachish. The Taylor Prism is now in the British Museum.
Assyria is an area located in Upper Mesopotamia, and named after the Assyrians.The Assyrians, a Semitic tribe, migrated to Upper Mesopotamia around 2,000 BC. For many years the Assyrians were overshadowed by the Sumerians and Akkadians. Ashur was the chief god of the Assyrians. Most of their cities were located along the Tigris River. The Assyrians built large palaces made of stone, which was available to them in Upper Mesopotamia.The Assyrians became an aggressive people under the rule of King Ashurnasirbal II.
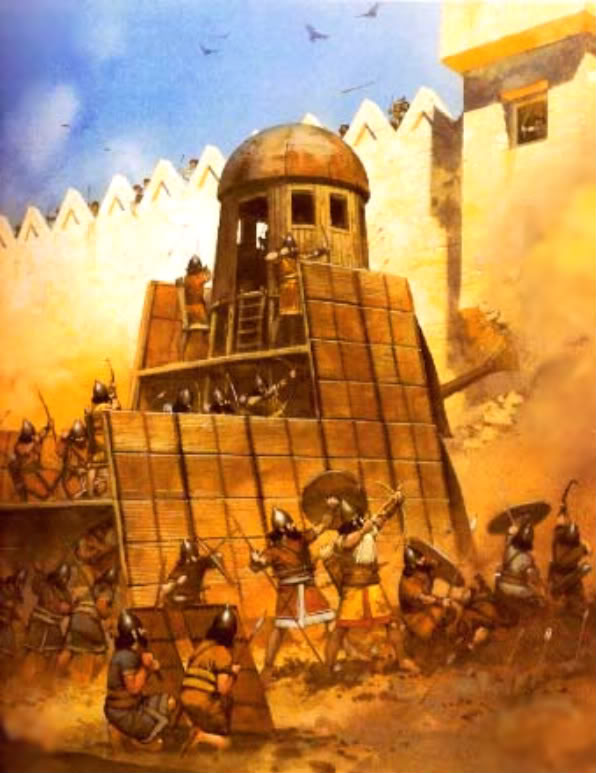
Ashurnasirbal, who reigned from 884 to 859 BC invaded the lands of his neighbors, his capital was the city of Nimrud, where he created the world's first zoo. Assyrian kings Tiglath-Pileser III and his son Sargon (same name, but not Sargon the Great of Akkad) continued Assyrian conquests by conquering Babylonia and the Kingdom of Israel. Sargon's son, Sennacherib, decided to lay siege to the city of Lachish in the Kingdom of Judah, because Hezakiah, the King of Judah, refused to pay Sennacherib tribute. Sennacherib was so pleased by the taking of the city, that he had a bas-relief made with illustrations and words showing the story of the conquest on his palace walls at the city of Nineveh. Nineveh had become an old worn-down city with much erosion from the river, but Sennacherib rebuilt the city, abandoning his father's brand new city that was almost complete when Sennacherib took the throne. Sennacherib bragged about his accomplishments with writings on a clay hexagon called the Taylor Prism.
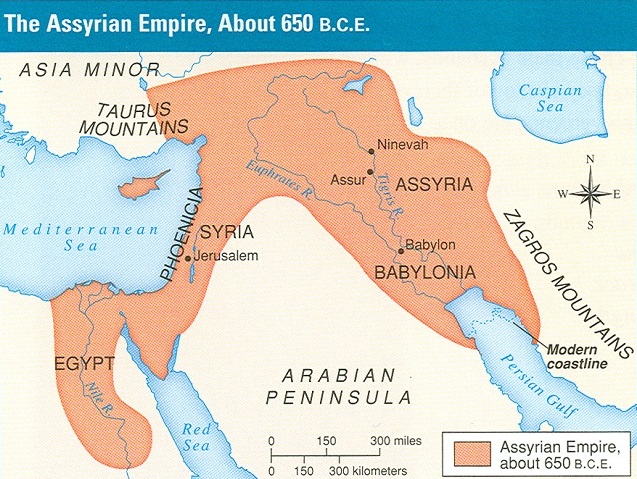
The Assyrian Empire: B.C.E. means "Before Christian Era," or "Before Common Era" On this map we can see that the Assyrian Empire was at its height about a thousand years after the empire of Hammurabi. Notice Asia Minor, the land of the Hittites. Which empire was larger, the Babylonian or Assyrian Empire?
Not long after the reign of Ashurbanipal, Assyria was invaded by the Medes and Babylonians, two groups of people the Assyians had conquered in the past. The Medes and Babylonians destroyed the Assyrian capital of Nineveh, including the Library of Ashurbanipal.
The Assyrians were amazing engineers, building stone palaces, changing the course of rivers, and creating wonderful gardens. After Assyria, Babylon had one more time of greatness, but it was short-lived. We will learn about the Neo-Babylonian Empire in the next chapter.
The siege of Lachish: The Assyrians had a professional army; a professional is paid for his or her services. Assyrian armies included spear-throwers, slingers, archers, and siege engines (battering rams and towers). Neighboring groups of people relied on farmers for their armies. Lachish was a city located near Jerusalem, you can see the location of Jerusalem on the Assyrian Empire Map. Jerusalem was the capital city of the Kingdom of Judah.
Source :
https://www.penfield.edu/webpages/ |