| PERGAMUM / PERGAMON Pergamum (or Pergamon to the Greeks), with its city and later kingdom situated near the Aegean coast of Anatolia, opposite the Island of Lesbos, was formed as a satrapy of the Persian empire from territory which had been under Lydia's control until 546 BC. Before that, the territory had traditionally formed the the southern section of Mysia, a Mycenaean-era kingdom. This southern area was was called Mysia Major or Pergamene, which gave Pargamum its own name. Mysia was apparently subsumed within the kingdom of Phrygia at the start of the twelfth century BC.
c.1200 - 695 BC :
Phrygia takes the territory which had previously formed Mysia and generally appears to control it during this period. However, Greek myth and legend ascribes the foundation of Pergamum to the eponymous Pergamus, son of the Greek warrior, Neoptolemos, and his concubine Andromache. During her old age, Andromache is said by legend to retire to Pergamum to live with her son after the death of her husband in Epirus. Pergamus is also the name of the citadel at Troy which had been destroyed by the Mycenaeans at the conclusion of the Trojan War, suggesting the possibility that the creation of a king called Pergamus is a substitution for a possible return by Andromache to the city of her birth, which has since been re-inhabited following the Trojan War.
fl c.1160s BC :
Pergamus : Legendary founder of Pergamum.
695 - 546 BC :
Phrygia loses the territory of Pergamum to Lydia about 695 BC, seemingly upon the defeat and suicide of King Midas III. Five years later, nomadic Cimmerian warriors overrun Phrygia and sack the capital, Gordion. However, this Cimmerian sacking is also stated to be the cause of Midas committing suicide, so the situation seems to be mildly confused. Either way, Lydia becomes the dominant power in western Anatolia whilst Phrygia is eclipsed.
546 BC :
Anatolia is conquered by the Persian empire, and the region becomes a satrapy.
Persian Satraps of Asia Minor / Eurypontid (Persian) Governors of Pergamum :
Conquered in the mid-sixth century BC by Cyrus the Great, the region of Pergamum was added to the Persian empire. Under Persian overlordship a satrap (governor) was installed to govern it, with what would appear to have been a generally peaceful transfer of power. Documentation for this period is poor, especially prior to the middle fifth century BC, and almost all dates are imprecise. This was not due to poor record-keeping, however, but to the general use of perishable materials such as papyrus. Many records that did exist were destroyed during the Greek takeover of the region in the fourth century BC and the subsequent years of in-fighting between them.
The first satrap whose name is known - Demaratus - was a king of Sparta who had been exiled for being obstructive and churlish (but perhaps a greater motive was his questionable parentage). He fled to Persia where he advised Darius I and then Xerxes on Greek affairs, and accompanied the Persian army in its invasion of Greece in 480 BC. Although that failed, Demaratus had proven his loyalty, so Xerxes made him governor of the cities of Pergamum, Teuthrania, and Halisarna within the province of Mysia, in the Lydian satrapy. His descendants inherited the office over the subsequent eighty years or so. Unfortunately, even records from this period have only partially survived.
(Information by Peter Kessler, with additional information from The Persian Empire, J M Cook (1983), from The Histories, Herodotus (Penguin, 1996), from The Cambridge Ancient History, John Boardman, N G L Hammond, D M Lewis, & M Ostwald (Eds), from Alexander the Great, Krzysztof Nawotka (Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2009), from Hellenica & Anabasis, Xenophon of Athens, and from External Links: Encyclopædia Britannica, and the Nabonidus Chronicle, contained within Assyrian and Babylonian Chronicles, A K Grayson (Translation, 1975 & 2000, and now available via Livius in an improved version), and Encyclopaedia Iranica.)
549 - 546 BC :
The Persian defeat of the Medes allows Cyrus the Great to conquer Anatolia between 549-546 BC. The people of Pergamum may even welcome the intervention of the light-handed overlordship of Cyrus over the potentially tighter controls of the defeated kingdom of Lydia. Any satraps who are appointed to administer the region in its early days as a Persian province are entirely unknown.
Cyrus the Great freed the Indo-Iranian Parsua people from Median domination to establish a nation that is recognisable to this day, and an empire that provided the basis for the vast territories that were later ruled by Alexander the Great Leonidas of Sparta achieves everlasting fame as a result of the events in the Battle of Thermopylae against the Persians in 480 BC. The Persian army is held up long enough for the Athenians to prepare their navy for a seaborne engagement with the Persian fleet. (These events are depicted somewhat colourfully - but no less impressively for that - in the 2007 film, 300, and its sequel).
480 - 479 BC : Much of the Persian navy is destroyed and Xerxes is forced to retreat to Asia, leaving his army in Greece. As a reward for his support of Xerxes during the war, the exiled Demaratus of Sparta is granted a minor satrapy of his own which includes the small cities of Pergamum, Teuthrania, and Halisarna.
479 - ? BC :
Demaratus : Satrap for Persia. Former king of Sparta (c.515-491 BC).
? BC :
? : Son. Satrap. Name unknown but presumed to succeed.
fl 450s/ 430s? BC :
Gongylos : Greek exile who governed the region.
450s or 430s? BC :
It is hard to provide a precise date for the governorship of Gongylos. A Greek exile, he serves on the Persian side during its invasion of Greece in 480 BC, and his widow, Hellas, meets the writer Xenophon in 399 BC. Coinage which could be attributed to him can be approximately dated to 450 BC. His governorship would seem to preclude a break in the hereditary rule of the Eurypontids. In 399 BC his sons, Gorgion and Gongylos the Younger, are between them governing four minor cities within Pergamum's territory but are clearly not senior governors.
? - 401 BC :
Cyrus the Younger : Brother of Artaxerxes II of Persia. In Pergamum & Sparda.
401 BC :
Cyrus the Younger, satrap of Asia Minor, attempts to revolt. He mobilises an army and ten thousand Greek mercenaries to attack his brother. The mercenaries cross northern Ebir-nāri and the Euphrates, but after Cyrus' death at the Battle of Cunaxa in October they return under the command of Xenophon.
The Battle of Cunaxa saw the end of just one in a number of internal Persian revolts that often involved thousands of troops on either side, although in this case the presence of a large body of Greek mercenaries should have been an indicator of the future threat the Greeks would become Along with his wife, Epyaxa, Syennesis of the client kingdom of Khilakku has supported the rebel army of Cyrus, primarily to protect his own lands from looting. Now his position may be untenable. Khilakku is reorganised as a formal satrapy within about a decade and its native kings are either removed or entirely sidelined, not to be mentioned again.
399 BC :
Xenophon reports that Eurysthenes and Prokles rule Pergamum, Teuthrania, and Halisarna. Although he doesn't directly link them to Demaratus, the fact that they are named after the two founding kings of Sparta is a good sign that this is the case. Another Prokles who is descended from Demaratus is said to marry Pythias, the daughter of Aristotle, and their sons are called Prokles and Demaratos.
fl 399 BC :
Eurysthenes : Probable descendant of Demaratus. Joint satrap.
fl 399 BC :
Prokles / Procles : Brother. Joint satrap.
c.300s BC :
Members of the Eurypontid family apparently return to Sparta in the fourth or third century BC. The usurper Nabis (202-196 BC) claims to be a descendant of Demaratus. In the fourth century BC, ethnic Persian satraps or appointed officials resume the task of administering the Pergamum region.
c.362 - 344 BC :
Orontes : Satrap of Mysia (including Pergamum).
c.362 BC :
Orontes is the Achaemenid-appointed satrap of the province of Mysia which includes Pergamum within its borders. Little information on him seems to be available, so it remains unclear whether Pergamum is governed directly by him.
334 - 333 BC :
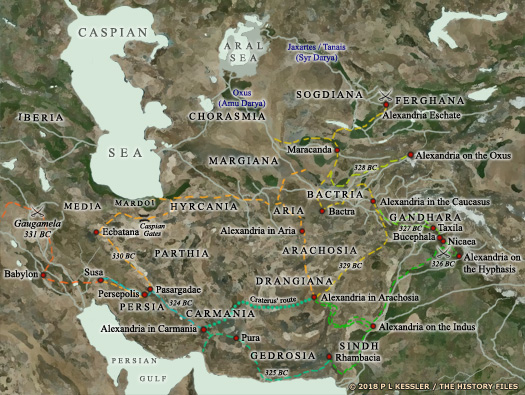
In 334 BC Alexander of Macedon launches his campaign into the Persian empire by crossing the Dardanelles. The first battle is fought on the River Graneikos (Granicus). The Persian defeat forces Satrap Arsites of Daskyleion to commit suicide. Sparda surrenders but Karkâ's satrap holds out in the fortress of Halicarnassus with the Persian General Memnon. The fortress is blockaded and Alexander moves on to fight the Lykian mountain folk during the winter when they cannot take refuge in those mountains.
Alexander the Great crossed the River Graneikos (or Granicus) in 334 BC to spark a direct face-off with the Persians that had been brewing for generations, and his victory in battle near the river sent shockwaves through the Persian empire The campaigning season of 333 BC sees Darius III and Alexander miss each other on the plain of Cilicia and instead fight the Battle of Issus on the coast. Darius flees when the battle's outcome hangs in the balance, gifting the Greeks Khilakku and Katpatuka, although pockets of Persian resistance remain in parts of Anatolia.
Argead Dynasty in Pergamon :
The Argead were the ruling family and founders of Macedonia who reached their greatest extent under Alexander the Great and his two successors before the kingdom broke up into several Hellenic sections. Following Alexander's conquest of central and eastern Persia in 331-328 BC, the Greek empire ruled the region until Alexander's death in 323 BC and the subsequent regency period which ended in 310 BC. Alexander's successors held no real power, being mere figureheads for the generals who really held control of Alexander's empire. Following that latter period and in advance of several wars, the small region of Pergamum (Pergamon to the Greeks) was left in the hands of the Antigonids from 323 BC.
The first satrap of Persian-controlled Pergamum had been an exiled king of Sparta who had fled to Persia. In return for providing accurate campaign advice for the 480 BC expedition into Greece, and for showing full loyalty, Xerxes had given him control of the cities of Pergamum, Teuthrania, and Halisarna. The region was overseen by the great satrapy of Sparda. His descendants inherited the office, although their position seems to have waned by the start of the fourth century BC. Little information seems to exist for the Argead period in regard to Pergamon. Principally this is probably due to it not being a satrapy as such, but an individual fortress (with surrounding town) that was only enhanced and expanded after the Argead period. A position of satrap didn't really exist until Philetaerus sided with the Seleucid empire in 282 BC well after the conclusion of the Argead period.
(Information by Peter Kessler, with additional information from The Persian Empire, J M Cook (1983), from The Histories, Herodotus (Penguin, 1996), from The Marshals of Alexander's Empire, Waldemar Heckel, from Alexander the Great and Hernán Cortés: Ambiguous Legacies of Leadership, Justin D Lyons, from A Political History of the Achaemenid Empire, M A Dandamaev, from Ctesias' Persica in its Near Eastern Context, Matt Waters, from Alexander The Great: In the Realm of Evergetǽs, Reza Mehrafarin, from The Cambridge Ancient History, John Boardman, N G L Hammond, D M Lewis, & M Ostwald (Eds), from Alexander the Great, Krzysztof Nawotka (Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2009), from Hellenica & Anabasis, Xenophon of Athens, and from External Links: Encyclopaedia Iranica, and Encyclopædia Britannica, and the Nabonidus Chronicle, contained within Assyrian and Babylonian Chronicles, A K Grayson (Translation, 1975 & 2000, and now available via Livius in an improved version).)
334
- 323 BC : Alexander III the Great : King of Macedonia. Conquered Persia.
323 - 317 BC :
Philip III Arrhidaeus : Feeble-minded half-brother of Alexander the Great.
317 - 310 BC :
Alexander IV of Macedonia : Infant son of Alexander the Great and Roxana.
334 - 323 BC :
? : Unknown Greek commanders of Pergamon for Alexander.
323 - 301 BC :
Upon the death of Alexander his two successors are retained as figureheads while the Greek empire is governed by Alexander's powerful generals. Perdiccas, the leading cavalry commander, is the first general to rule, carrying the title 'Regent of Macedonia', first with Meleager, head of the infantry officers, as his lieutenant, but alone after he has him murdered. In the first of many rounds of reorganisation, Antigonus Monophthalmus gains Pergamon as part of his Antigonid holdings. If a commander is appointed to govern Pergamon, his name seems not to have survived in written records.
The route of Alexander's ongoing campaigns are shown in this map, with them leading him from Europe to Egypt, into Persia, and across the vastness of eastern Iran as far as the Pamir mountain range 323 - 301 BC :
? : Unknown Greek commanders of Pergamon for the Antigonids.
308 - 301 BC :
The Fourth War of the Diadochi soon breaks out. In 306 BC Antigonus proclaims himself king of his Antigonid empire, so the following year the other generals do the same in their domains. Polyperchon, otherwise quiet in his stronghold in the Peloponnese, dies in 303 BC and Cassander of Macedonia claims his territory. The war ends with the death of Antigonus at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BC, by which time Philetaerus has already switched his allegiance to the Lysimachian side (in 302 BC).
301 - 282 BC :
Philetaerus : Greek commander of Pergamon for the Lysimachians.
301 - 282 BC :
With the death of Antigonus in 301 BC, Pergamon falls under the rule of the Lysimachian empire. By this time Lysimachus seems already to have gained control of the fortress of Pergamon, placing Philetaerus there as its commander. This effectively means that he commands Pergamon as a whole, small territory though it is. He remains in this position until 282 BC when he defects to Seleucus whose Seleucid empire allows him a far greater degree of regional control. In effect, at this point the Attalid dynasty of local rulers can be said to be formed, which soon achieves full independence.
Attalid Kings of Pergamon :
The ancient Greek city of Pergamon was taken by Lysimachus, king of Thrace, in 301 BCE, a short-lived possession that ended when the kingdom of Thrace collapsed. Pergamon was ruled as a Hellenic domain of the Lysimachian empire during Philetaerus' lifetime, which was created by one of Alexander the Great's generals after the collapse of the Greek empire. The city was turned into a fortress and was selected to house many of the Lysimachian riches. It was only with the later success of Attalus against the Galatian Celts that an independent kingdom was proclaimed in 230 BC, although it still remained within Greece's sphere of influence. It later became a loyal ally of Rome, fighting alongside the Romans against the Macedonians.
(Additional information from The Marshals of Alexander's Empire, Waldemar Heckel, and from External Links: University of Leicester, and Listverse, and Virtual Religion: Into His Own, and Encyclopædia Britannica, and Pera: Ancient Pergamum.)
282 - 263 BC :
Philetaerus : Greek satrap of Pergamon. One of Lysimachus' officers.
263 - 241 BC :
Eumenes I : Nephew. Greek satrap of Pergamon. Independent c.262 BC.
c.262 BC :
Antiochus I of the Seleucid empire attempts to break the growing power of Pergamon. He engages the forces of Eumenes I in battle near Sardis but is defeated and dies soon afterwards. The reason for his death seems unknown but battle wounds could be a reasonable cause. Eumenes is able to establish Pergamon as an independent city state.
241 - 197 BC :
Attalus I / Attalos I Soter : First cousin. Greek satrap of Pergamon. Declared a kingdom.
235 - 229 BC :
Antiochus Heirax continues his campaign to wrest the Seleucid empire from his brother by defeating him at the Battle of Ancyra in 235 BC. However, Attalus of Pergamon is instrumental in foiling his ambitions, especially when he is victorious at the Battle of Harpasus in 229 BC. Antiochus is forced out of Anatolia and eventually ends up in Egypt (where he is killed by robbers around 226 BC).
230 BC :
Attalus triumphs against the Galatian Celts and subsequently proclaims himself king, pulling the territory out of the control of Macedonia.
223 BC :
Seleucus III is campaigning for the second time in his reign against Attalus I as part of the ongoing struggle to recover control of Anatolia. For whatever reason he is assassinated by generals in his army, perhaps due to his poor showing on the battlefield. The Seleucid empire is in a perilously weak position.
222 - 220 BC :
Antiochus III sets about rebuilding the Seleucid empire which is shown to be very weak at this time. Although both his own first campaigns end in disaster, in the north, Achaeus, his cousin, records the only immediate success by forcing Pergamon back to its original borders. However, Achaeus rebels in 220 BC, proclaiming himself king in Anatolia in the fashion of his predecessor, Antiochus Heirax, before him. Antiochus is not yet strong enough to face him and a revolt within his own forces prevents him from advancing southwards.
216 - 213 BC :
Now strong enough to face his rebellious cousin, Antiochus III of the Seleucid empire is able to march his forces into western Anatolia. By 214 BC Achaeus has been driven back to Sardis where he is captured and executed. The citadel itself is able to hold out until 213 BC under Achaeus' widow Laodice. Central Anatolia has been recovered but several regional dynasties persist in Bithynia, Cappadocia, and Pergamon. Rather than try his hand against these, Antiochus concentrates on the northern and eastern provinces of the empire. Xerxes of Armenia is persuaded to acknowledge his supremacy in 212 BC, while in 209 BC Antiochus invades Parthia. Its capital, Hecatompylos, is occupied and Antiochus forces his way into Hyrcania, with the result that the Parthian king, Arsaces II, is forced to sue for peace.
200 - 196 BC :
The Second Macedonian War is triggered by claims made by Attalus of Pergamon and also by Rhodes of a secret treaty between Macedonia and the Seleucid empire that is designed to carve up Egypt's possessions. Rome launches an attack against Philip V of Macedonia and after a spell of indecisive conflict, Philip is defeated at the Battle of Cynoscephalae in 197 BC. His general, Androsthenes, is defeated near Corinth, while parts of Pergamon are occupied by Antiochus III of the Seleucid empire in 198 BC. The Macedonian army is drastically reduced in size as a result of the defeat, and Philip's standing as an important Greek king is greatly diminished.
197 - 160 BC :
Eumenes II : Son.
190 - 188 BC :
Rome defeats the Seleucids in the Seleucid War, taking Asia Minor as a province in 188 BC. The Seleucid ally, Cappadocia, negotiates friendly terms with Rome, notably because Stratonice, the king's daughter, is about to marry the king of Pergamon, a Roman ally. Pergamon annexes Lydia and Pamphylia around this point in time.
183 - 180 BC :
Further expansion of the kingdom takes place when the Thracians are occupied with support from Cappadocia. However, this tough mountainous terrain is too difficult to hold, and within three years, Macedonian supremacy there has been restored.
160 - 138 BC :
Attalus II Philadelphus : Brother.
138 - 133 BC :
Attalus III : Son of Eumenes II.
133 BC :
Attalus bequeaths the state to Rome to avoid a likely succession crisis. The Romans are slow to take up their claim, so the illegitimate Eumenes III fills the power vacuum and tries to gather support.
Pergamon rose to prominence during the years of division in the Greek empire following the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC when his empire was divided among his generals - now it worked in tandem with Cappadocia 133 - 129 BC :
Eumenes III Aristonicus :
131 - 130 BC :
The first Roman army to be sent against Eumenes is joined by allies from the kingdom of Cappadocia. The attempt meets with failure when the combined armies are defeated. Both Proconsul Publius Licinius Crassus Dives Mucianus and King Ariarathes V of Cappadocia are killed.
129 BC :
Eumenes is defeated and captured by a second Roman army. He is paraded through Rome and then executed by being strangled. Pergamon is incorporated into the Roman republic and its successor, the empire.
Source :
https://www.historyfiles.co.uk/ |