ANCIENT
EGYPTIAN SYMBOLS

Popular
Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphic Symbols And Meanings
To
better understand why Ancient Egyptians used Amulets or Symbols
during their life or in sarcophagus and tombs, we must know about
their beliefs.
The Ancient Egyptians believed that their life on earth is temporary,
but the permanent one is after their death and after passing the
12 Portal of the World of death. They were sure that they would
come back to life like everything around them, The Nile, the Sun,
and even plants; they disappear then appear again.
For Egyptians, the human being consists of the Body "Khet,"
Consort or "ghost" "Ka'', Heavenly Spirit "Ba,"
Name "Ren," & the Heart "Ib". When coming
back to life, they will need a complete body, so they went to
the Mummification, so the Ka & the Ba could find the body.
The name was also essential to help them recognize death; that's
why they invent the "Cartouche".
The Heart will be left in the mummified body to witness with or
against the disease during the second world's last judgment. So
they invent some amulets to force the heart to be with the deceased.
The long Egyptian History is full of legends like World Creation,
Isis & Osiris, or some deities. We Will Review Here The Most
Popular Symbols in Egyptian Civilization.
What Does Each Egyptian Symbol Mean ? :
1.
Canopic Jars
2. The Ankh
3. The Scarab Beetle
4. Eye of Horus
5. Eye of Ra
6. Hekha and Nekhakha (Crook and Flail)
7. Uraeus
8. Lotus Symbol
9. Nemes Headdress
10. The Ka
11. The Red Crown "Deshert"
12. The White Crown "Hedjet"
13. The Double Crown "Pschent"
14. Blue Crown "Khepresh"
15. Ouroboros
16. Menet (Menat, Menit)
17. Djed
18. Ajet
19. Cartouche
20. Tree of Life
21. Bennu Bird
22. Crescent
23. Seba
24. Sistrum
25. Amenta
26. Feather of Maat
27. Was Scepter
28. Tyet (Knot of Isis)
29. Shen
1.
Canopic Jars Symbol :

Canopic
Jars
Ancient Egyptian believed that death is the first step toward
resurrection and eternal life; that's why they were making sure
to save their bodies from any corruption after death by mummification.
What Canopic Jars Are Symbolize, And What The Jars Used
To Protect? :
A set of four embalming jars symbolizing the four sons of Horus,
each Jar protects an organ belonging to the Deceased. They used
to move out all the body's internal organs except the heart, as
they believed it's the soul's seat. And they were embalming the
intestines, lungs, the stomach, and liver, then wrapping them
with linen and keeping each organ of them in a separated Canopic
Jar.
Each
Jar has a headed lid representing one of Horus's sons, and each
has a specific organ to keep safe.
•
Hapi, the baboon-headed god, guards the lungs.
• Duamutef, the jackal-headed god, guards the stomach.
• Imsety, the human-headed god, guards the liver.
• Qebehsenuef, the falcon-headed god, guards the intestines.
2. The Ankh (Key Of Life) :

Ankh
Key of Life
Ankh symbol is the most common decorative motif in ancient Egypt
and by neighboring cultures, as an Egyptian symbol of protection
and other things.
How
was The Ankh symbol shaped? :
The
most commonly used and known symbol since the early Dynasty is
the Ankh; you probably know it by life's key. It's an ancient
Egyptian symbol that looks like a cross with a looped top in a
teardrop's shape; it is one of the Egyptian characters most commonly
used in tattoos.
What
Is The Ankh symbol used In Ancient Egyptian? :
This symbol was used in Hieroglyphic writing and Egyptian art
to represent the word "life," you'll find it a lot in
the tomb paintings and inscriptions on the temples' walls, so
it is one of the Egyptian symbols used in the alphabet. The Egyptians
also wore it as an amulet, so it is a symbol for protection.
What
Ankh symbolizes, and Why was it held in the ancient Egyptian deities?
:
The Ankh symbolizes many things like the power to sustain life
and revive human souls in the afterlife; that's why it was commonly
held in the hands of ancient Egyptian deities or given by them
to a pharaoh. It also symbolizes the promise of eternal life,
the Sun, fertility, and light. The symbol was placed among the
mummy wrapping to secure the deceased's rebirth and well-being
in the afterlife.
The
mystery behind the Ankh symbol :
This symbol's origin is still a mystery; one theory says it originated
from a sandal strap. Others suggest it was the belt buckle of
goddess Isis, but we certainly know it is associated with life.
3. The Scarab Beetle :

Scarab
Beetle
The Egyptian Scarab beetle, one of the most common symbols in
ancient Egypt and the most popular, was worn by the living and
the dead as an Egyptian symbol of protection and death.
Where
did the Beetle Scarab come from? :
The Scarab beetle comes from a species of the dung beetle. The
idea came from rolling the dung into a ball and laying its eggs
in it, and when the eggs hatched, the dung was served as food
for them. When Egyptians saw this phenomenon, they immediately
associated the Scarab Khepri with the sun god Ra as his assistant
because scarabs roll large balls of dung to lay their eggs. Hence,
they thought this resembles the progression of the Sun through
the sky from east to west.
What
does the scarab beetle symbolize and represent in ancient Egypt?
:
Scarab is the symbol of death, rebirth, immortality, and protection
in the afterlife; it is much used in funerary art; later, it referred
to the idea of existence, transformation, and divine manifestation.
4. Eye of Horus :

Eye
of Horus
The Eye of Horus is one of the most famous Egyptian Symbols; today,
we use it in jewelry and paintings. It is a widely used Egyptian
Symbol in tattoos. The left eye of Horus represents protection,
health, and restoration, so it is an Egyptian symbol of protection.
What
does the Eye of Horus symbolize? :
Another story says that Horus took his left eye out for his father
Osiris to eat to bring him back to life. In both stories, the
Eye was a symbol for healing and being whole again. Although the
ancient Egyptian civilization came to an end, the belief the Eye
of Horus energy continued and still used. It's usually made of
gold, lapis lazuli, and carnelian mainly.
What
is the Hieroglyphic meaning of the Eye of Horus? :
Also, in hieroglyphic writing, the Eye of Horus was used as a
mathematical symbol; every part of the six represents a measurement
unit. Ex: the right side equal ½, the pupil ¼, the
eyebrow 1/8, etc. More fractions were created by adding parts
together. The most interesting is by adding all parts, the result
is 63/64 and never 64/64. The missing piece represents the magic
Power of Thot or the fact that nothing is perfect.
The
Myth behind the Eye of Horus and its meaning :
According to Osiris and Isis' famous Myth, when Horus reached
adulthood, he thought to avenge his father's death; he fought
his uncle Set, and during the battle, Horus lost his left Eye
that broke into six pieces. Thot, the god of Wisdom, magically
restored Horus's Eye, and then it became known as "Wadjet':
which means ''whole or "healthy, "and they started to
believe it has healing power. Due to its protective and healing
power, Horus’ Eye was used as an amulet for living and dead.
5. Eye of Ra :

Eye
of Ra
The Eye of Ra is a symbol of authority and protective powers.
It is associated with the Sun God Ra. Although it is associated
with the destructive power of the Sun, it was used to protect
buildings and people, so it is an Egyptian symbol of protection.
What
is the difference between the Eye of Ra and the Eye of Horus? :
The Eye of Ra is differentiated from Horus' Eye by drawing it
as the right Eye. It is more powerful than Horus, as Ra's Power
of vision is unlimited. Ra was one of the most powerful gods in
Ancient Egypt; that is why his eyes "can see everything.”
What
is the Myth behind the Eye of Ra? :
Egyptians believe that Ra took his sun-boat every day when the
Sunset into the water and passed the 12 gates of the Underworld
in the 12 hours of the night, then came back in the morning. That's
why they used to build their tombs on the left side of the Nile
to enable the deceased to accompany Ra during his trip in the
netherworld so he won't stay in darkness.
A myth tells that Ra sent his Eye to watch over his children and
protect them. Another one tells that when Ra became an old god,
men maltreated him, so he sent his Eye or his daughter to punish
humanity. The daughter raged and began to destroy humanity, but
Ra, to rescue humanity, gave his Eye a red bear until it came
drunk, peaceful, and returned to him.
Sometimes the Eye of Ra was depicted as the sun disc encircled
with two cobras.
6. Hekha and Nekhakha (Crook and Flail) :

Crook
and Flail
The
crook is known in ancient Egypt as The Heka; its early use was
by shepherds to control his sheepfold. The Flail was known as
the Nakhakha, also has a farmer origin, and it symbolizes the
King’s power as it was a source of punishment to maintain
order in society. The Flail is considered an Egyptian symbol of
strength. They both date back to the Early dynastic period during
the rule of the first king, Narmer.
What
do the Crook and Flail symbolize? :
The Crook and Flail are symbolic of Kingship, signifying the Pharaoh's
dominion over Egypt’s land and Egyptian royalty symbols.
They are seen with every King and Queen who ever ruled Egypt.
They also symbolized that the Pharaoh is the shepherd for his
people and provided them with food. They were usually made of
wood and covered with gold.
Why
did Pharaohs carry a Crook and a Flail? :
Crook and Flail were associated first with Geb, the god of earth,
and Osiris inherited them. Hekha and Nekhakha were usually put
with the Pharaoh in its tomb; he held them in both hands in a
cross form on the chest to symbolize the divine authority.
7. Uraeus (Ancient Egyptian Cobra) :

Uraeus
or Cobra
Uraeus, or the Cobra, is one of Egypt's most ancient symbols.
It was the emblem of Lower Egypt. It was an Egyptian goddess symbol
that represented the Goddess of Royalty and sovereignty, Wadjet.
The Cobra was believed to have magical powers, and its presence
on a royal crown means "Protection of enemies." Geb,
the god of the earth, gave it to the pharaohs as a sign of Kingship;
therefore, it was an Egyptian symbol of protection.
What
is the Myth behind the Uraeus? :
The first Myth is connected to the origin of Uraeus in the Story
of Ra; it is believed that goddess Isis made the first one from
the dust of the earth and the spittle of Sun to acquire the throne
for her husband, Osiris. Later, it was seen on the Kings' crowns,
and the most famous is one of Sensuret II; it was made of solid
gold and black granite eyes measuring 6.7cm in length.
8. Lotus :

Lotus
Symbol
It’s a symbol of Upper Egypt; it appeared bonded to the
Papyrus as a sign of unification of the two Egyptian kingdoms,
the upper and lower. It was also associated with the Sun God Ra
and later with Nefertum, the god of healing, medicine, and beauty.
What
does the Lotus Symbol mean? :
The Lotus flower was called 'Sesen' in the Egyptian language;
it is considered an Egyptian symbol in the alphabet. It wasn't
only famous in ancient Egypt; it is also popular in Buddism and
Hindusim. The Lotus Symbol was associated with purity and cleanliness,
also a symbol of Sun, creation, and rebirth.
Where
was the Lotus Symbol found? :
The Lotus flower is an ancient Egyptian symbol found a lot among
hieroglyphic writing in tombs, on Papyrus, thrones, and the headdress
of divine pharaohs. It was also found in the book of death; there
is a magic charm that can transform the dead into a Lotus flower,
thus allowing his resurrection.
What
are the types of the Lotus flower? :
There were two types of the lotus flower in ancient Egypt, the
white and the Blue (the water lily), and at a later time, the
pink one came to Egypt from Persia.
What
does the Lotus Flower symbolize? :
As the Lotus flower retracts into the water at night and then
emerges the next day, it is associated with the Sun, which disappears
in the night and re-emerges in the morning. That's why it was
a symbol of rebirth and regeneration. It is also an Egyptian symbol
for love, as the lovers gave it to each other as a token for their
love.
9. Nemes Headdress :

Nemes
Headdress
Remember
the famous Golden mask of King Tut Ankh Amen? The boy-king was
wearing a Nemes Headdress. It is a fabric head-cloth of Blue and
gold reaching the shoulders and was worn by ancient Egypt's rulers.
What
does the Nemes Headdress symbolize? :
The Nemes dates as far back as the third Dynasty during the reign
of King Djoser. The fourth Dynasty became the Royal Headdress,
so it became an Egyptian symbol of Royalty. Later, Nemes’
use became a funerary representation of the Royal Ka, and it was
worn by goddess Isis & Nephthys while performing their roles
of mourners.
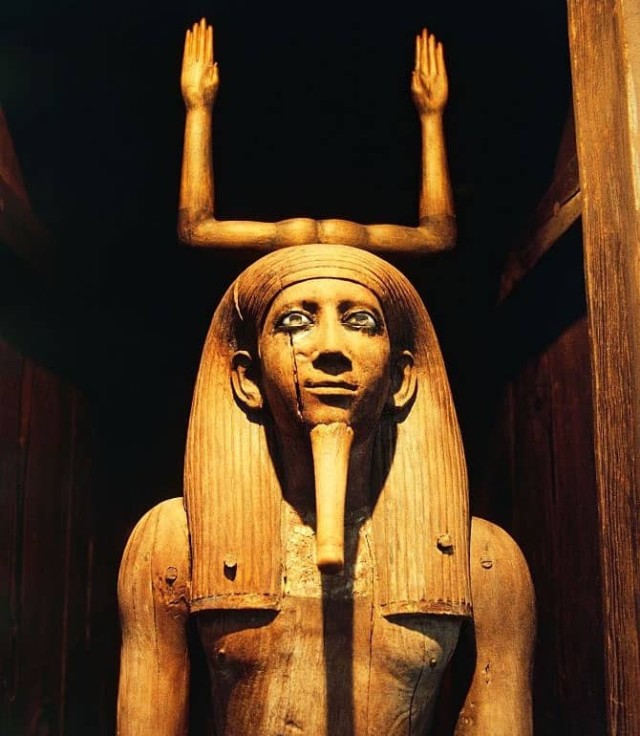
10. The Ka :

Ka
Statue
What does the Ka mean? :
The Ka means soul or spirit; it was like a person's twin live
inside his body until death. After death, the Ka would leave the
body, but not for good. If the body is well preserved, the Ka
would return to it again and lead him through the 12 portals of
the infernal world till the resurrection. That's why ancient Egyptians
were mummifying the deceased's body so that the Ka could recognize
him and find its way back to it. Because the "Ka" remains
alive, they put food and drinks inside the tomb to find what it
needs to go through resurrection.
What
is the Ka represented with? :
The Ka is usually represented by two arms reaching up to the sky
in the ancient Egyptian language.
11. The Red Crown "Deshret" :
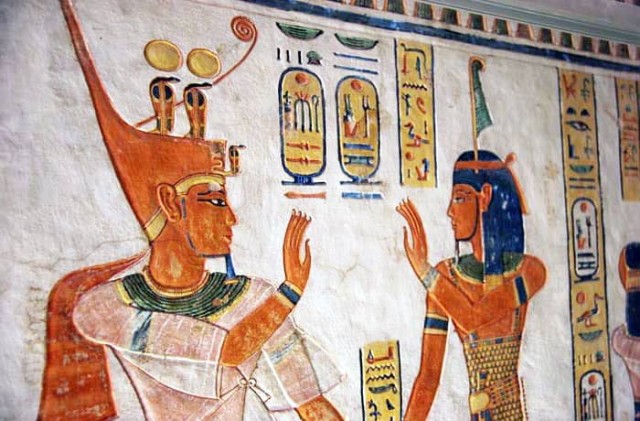

Deshret
Red Crown
Once Egypt was divided into two kingdoms; Lower Egypt, the Kingdom
of the north, around Nile Delta, and Upper Egypt, the Kingdom
of the south. Each Kingdom has its Crown; the Red Crown belongs
to the Lower Egypt Kingdom. Some gods and goddesses were depicted
wearing this Crown to show that the ruler was blessed and protected
by gods.
What
does the Red crown symbolize? :
The Deshret symbolized the authority over Lower Egypt for whoever
wears it. The Red Crown distinguishes the King's Forehead with
the Cobra, the Egyptian goddess symbol of "Wadjet,"
the protector of Lower Egypt.
12. The White Crown "Hedjet" :
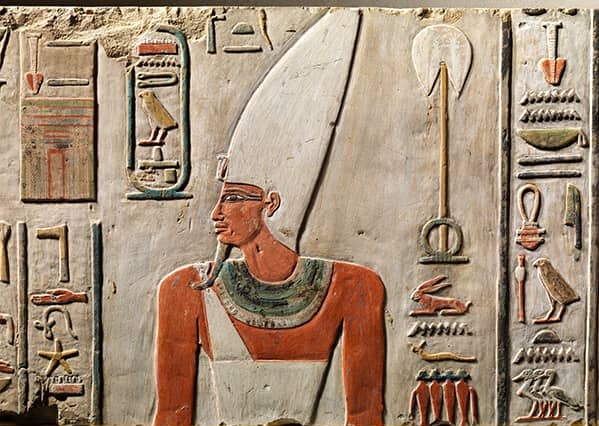

The
White Crown Hedjet
What is the Hedjet, and what does it symbolize? :
The Crown of Upper Egypt, the South Kingdom, around the Nile Valley
from south of Memphis to Aswan. It has a conical shape with white
color, an Egyptian symbol of Royalty and Upper Egypt; later, it
was combined with the Red Crown "Deshret."
Who
in Egypt wore the Hedjet? :
The vulture Goddess Nekhbet was mostly depicted wearing it and
the Falcon God Horus as well. While the King was wearing the White
Crown, Nekhbet, the Vulture goddess, sometimes distinguished the
King's forehead as upper Egypt protector.
13. The Double Crown "Pschent" :

The
Double Crown Pschent
What does the Pschent symbolize? :
It was a symbol of unified Egypt, and Kings usually wear this
Crown to show their control all over Egypt and as an Egyptian
symbol of Royalty. When King Menes or Narmer unified Egypt in
the 2nd Dynasty (about 3200 BC) and became the King of North &
South Egypt, the Crown of the ruler became a combination of Crowns,
the Red and White, which symbolized Lower and Upper Egypt.
14. Blue Crown "Khepresh" :

Blue
Crown Khepresh ancient egypt symbol of war ramses II wearing it
to celebrate his victory over the Hittites
What does the blue crown "Khepresh" represent and symbolize?
:
Khepresh is known as the War Crown, and its blue color represents
the sky. Kings of the New Kingdom wore this crown during their
wars as a symbol of sky protection and as an Egyptian symbol of
Royalty. The first one was made for the Pharaoh Amenophis III,
which is considered to be the evolved version of the cap crown.
On the other hand, archeological prove that it dates back to the
Second Intermediate Period, as shown on Karnak Stela of Neferhotep
III.
What
was the blue crown made of? :
The Khepresh was made from rubber or cloth painted blue, adorned
by golden discs and a twisting Uraeus – goddess Wadjet-
in the front.
When
was the blue crown worn? :
The Blue crown was mainly worn in wars, but Ramses II was painted
wearing it to celebrate his victory over the Hittites, then it
became a ceremonial crown of the King.
15. Ouroboros :

Ouroboros
What is the Ouroboros? :
The "Ouroboros" is one of the most significant &
unique Egyptian symbols in Ancient Egypt. The Egyptian name for
it was "Sed m ra" which means "tail in the mouth,"
It depicts a serpent with its tail in its mouth continually devouring
itself and reborn from itself.
What
does the Ouroboros symbolize? :
This is the symbol of rebirth, perpetuity & immortality used
in Egypt since 1600 B.C. It first appeared in King Tut's Tomb
as a part of the book of the netherworld in the 14th century B.C.
What
does the Ouroboros mean? :
Ouroboros also has several meanings. The lower part of it symbolizes
the destructive force of nature, the night, and the yin. The Upper
part symbolizes the generation, creative force, the day, and the
yang.
This symbol entered the Western World via some magical Papyrus.
The name "Ouroboros" is a Greek name that means "devouring
tail" and symbolizes Eternity "The Beginning & The
End."
What
was the Ouroboros symbol used for? :
It was a very popular symbol during the Roman era; it was used
in magical talismans and emblems. It is one of the Egyptian symbols
used as a tattoo nowadays.
16. Tree of Life :

Tree
of Life
What is the Tree of life? :
The Tree of life is the most important symbol in Ancient Egypt's
mythology. Many cultures and beliefs widely know it, but the ancient
Egyptians were the ones who provided the oldest concept of this
symbol.
What
does the Tree of life symbolize? :
The Tree is located at the Sun Temple of Ra, the god of Sun, at
Heliopolis; it represents Ra's soul, symbolizing the resurrection
and the rising Sun. The fruit of this Tree guarantees eternal
life and knowledge of the cycles of time, as the Tree holds the
knowledge of the divine plan or the map of destiny. That's why
this fruit wasn't for mortal persons; it was only available in
the ritual in which gods refresh Pharaoh's aging or symbolize
the Pharaoh's unification to gods, so it is an Egyptian religious
symbol.
What
is the Tree of life also known with? :
It is also connected with the Myth of creation and the nine gods
of the Ennead of Heliopolis. The Tree of life is also known as
the sacred mythical Ished Tree, the Bennu Bird (Phoenix) home.
What
was the Tree of life used for? :
During the coronation ceremony of a Pharaoh coronation, god Thot
– the god of Wisdom – wrote the King's name on its
leaves and fruits to protect the King and perpetuate his name.
Later myths tell the story of god Osiris who was killed by his
brother Seth – the evil god – and put him in a coffin
and then threw him in the Nile. The coffin became embedded in
the base of the tamarisk, "the tree of life."
17. Bennu Bird :

Bennu
Bird
What
is the Benu Bird? :
You might know the Bennu bird from Harry Potter as the Phoenix
that burned itself to flames then rise from its ashes. The Bennu
Bird is an ancient Egyptian symbol connected to Ra, the Sun god's
soul, and took the City of Heliopolis as its headquarter.
Where
did the name Benu come from? :
The name Bennu came from "Weben" in ancient Egypt, which
means "to rise" or to raise brilliant," also might
be the Egyptian goddess symbol for the goddess of motherhood.
What
does the Benu Bird represent? :
The Tree of life is the Bennu Bird seat; they both represent the
concept of resurrection and the rising Sun. It was believed that
the Bennu bird visits the temple once every 500 years and burns
itself to ashes when it reaches 1461 years old.
18. Menat (Menet or Menit) :

Menat
Menet Menit
What does the Menat symbol mean? :
Menat is a necklace associated with the Goddess Hathor and her
son Ihy since the sixth Dynasty and had strong religious meanings.
Who
used the Menat? :
Hathor used this necklace as a medium for transmitting her Power.
The Menat was used only by the elite in Ancient Egypt. The necklace
appeared during the New Kingdom in King Tut Ankh Amen's Tomb.
What
was the shape of the Menat, and what was it used for? :
The Menat is a necklace with a crescent front, heavy collar, and
counterweight at the back to keep in the position; it was used
as a percussion instrument in religious functions.
What
does the Menat symbolize? :
It is considered an Egyptian religious symbol; it symbolizes fertility,
birth, life, and renewal. According to Hathor, part in the rebirth
of the dead and her duty as the goddess of the western necropolis,
Hathor was sometimes called "the Great Menat." The Menat
was seen after other goddesses, Isis and Nut, in their bovine
forms.
19. Djed :

Djed
What does the Djed mean and symbolize? :
The Djed is a famous Egyptian symbol; it was a symbol of stability;
it was used in the Egyptian alphabet with that meaning. It is
also the Egyptian goddess symbol for Osiris, usually known as
the "Backbone of Osiris." It was first associated with
the God Ptah and symbolized creation; he usually appeared carrying
a Scepter which combined the Djed and Ankh.
What
is the shape of the Djed? :
It consists of a column with a broad base that narrows as it rises
to capital and is crossed by four parallel lines; the Egyptians
believed they held the four corners of the earth.
What
is the origin of the Djed? :
The Djed is widely featured on pillars, tomb walls, and palace
walls and painted on Papyrus. The origin of the Djed is unknown,
but it first appeared in the Predynastic Dynasty till the last
Dynasty in Egypt, before becoming a province in the Roman Empire.
Later it was strongly associated with God Osiris and his return
from death. The Djed is from the Egyptian symbols that are commonly
drawn as a tattoo nowadays.
20.
Ajet or Akhet :
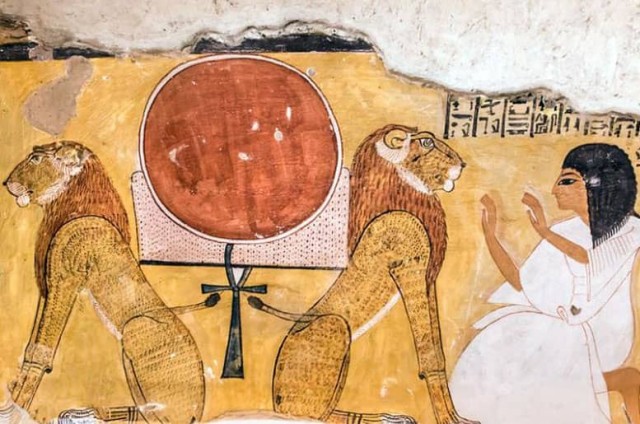

Ajet
Akhet
Ajet is an ancient Egyptian symbol used in hieroglyphs writing;
considered an Egyptian symbol and an alphabet.
What
does the Ajet represent? :
It represents the Sun on top between the summit of two mountains
and two lions protecting it. The two mountains are the Western
and eastern sides of the Egyptian underworld, and lions represent
Aker, the god of the underworld; they represent yesterday and
today. The symbol shows the natural phenomenon of the sunrise
and Sunset.
What
does the Ajet symbolize? :
The Ajet symbolizes the concept of creation and rebirth.
21. Cartouche :

Cartouche
What is the Cartouche used for? :
The Cartouche was a nameplate or a seal used by all ancient Egyptian
Pharaohs; It was an oval with a straight line at one end; it was
initially circle-shaped, presenting the Sun on the horizon and
containing King's name in the middle. This name tag wasn't only
to identify the King, but it was also a powerful amulet protected
from the evil spirits by being connected to the Sun.
What
does the Cartouche symbolize? :
A Cartouche is an Egyptian symbol of protection and the guide
to the deceased's souls, Ka and Ba, to reach their body when coming
back to life. It represented Good Luck and protection from evil.
In Hieroglyphs, it was used for the word "name."
22. Crescent :

Crescent
What does the Crescent symbolize? :
The moon crescent was one of the most powerful luck symbols in
ancient Egypt. It is a symbol inspired by Isis – all gods'
mother – so she is the goddess of motherhood, fertility,
healing, and magic. The Crescent was used to bring good fortune
to the mothers and their children, so it is an Egyptian symbol
for the family.
23. Seba :

Seba
What does Seba mean? :
Seba is the symbol of the star that looks like a starfish. It
is one of the Egyptian symbols in the alphabet; it means "learning"
or "discipline."
What does Seba represent? :
According to Ancient Egyptians beliefs, Seba was associated with
doorways and gates in the world of death. When Seba is enclosed
in a circle, it represents Duat or the other-world, where the
Sun disappears each night, and the Dead's souls ascend after death.
It's where the deceased person passes to reach Osiris, the god
of the world of death.
What was the Seba used for? :
In daily life, Stars were significant to the ancient Egyptians;
they made their calendar according to them.
24. Sistrum :

Sistrum
What is a Sistrum? :
The Sistrum is one of the most ancient and sacred musical instruments.
It has the shape of the Ankh with small movable rings made from
bronze or brass to make sounds.
What was the Sistrum used for? :
The name Sistrum is derived from the sound it makes. It was used
in religious ceremonies, so it is considered an Egyptian religious
symbol. It was mainly used for the cult of Hathor; it is believed
to get the attention of the gods and goddesses, sometimes to frighten
Seth, and other times to prevent the flooding of the Nile.
The Sistrum was mainly used in the worship of Hathor; that's why
one of the most popular presentations is in the Dendera temple.
Later, it was seen with Isis and Bastet as well. It was also used
by shaking it to avoid the flooding of the Nile.
25. Amenta :

Amenta
What does the Amenta symbolize? :
Amenta is the symbol of the Underworld, and it represents the
horizon where the sunsets are. It symbolizes the Nile's West Bank
that was used as a burial place. The West Bank for Ancient Egyptians
was the Land of the dead as the Sun disappeared on this side.
It's where the journey of the afterlife begins. Amenta is the
symbol of the Underworld or the Duat; thus, it was found abundantly
in the book of death.
26. Feather of Maat :

Feather
of Maat
What is the feather of Maat, and what does it symbolize? :
Maat is the Ostrich goddess who set the world in order upon its
creation. So she became the goddess of order, balance, well-being,
and justice. Maat also symbolized moral & ethical values.
The Feather of Maat is a significant symbol in Ancient Egypt;
it is the Egyptian goddess symbol for Maat herself, symbolizing
the same morals.
The only one found in a tomb of a dead Pharaoh was the one found
with Tut Ankh Amun, as it also was an Egyptian symbol of Royalty
and strength.
What was the feather of Maat used for? :
The feather of Maat was used in the judicial process in the Hall
of Two truths; the deceased's heart was weighed against the feather.
If the heart equaled or were less than the feather's weight, he
would join Osiris in the Underworld. If the heart outweighed the
feather, it would be eaten by Ammit, and he would be cursed.
This Egyptian symbol was also used in the alphabet, in the context
of "ensuring justice," also an Egyptian symbol of love.
27. Was Scepter :

Was
Scepter
What does the Was Scepter symbolize? :
"Was Scepter" is an ancient Egyptian symbol for strength,
widely used as a symbol of sovereignty, and in Hieroglyphic writing
to represent" Power," it was also the symbol of Thebes.
Sometimes the "Was" scepter was associated with the
"Heqa" or "Heq Scepter," the symbol of divine
power and authority.
What is the shape of the Was Scepter? :
The Was Scepter was a staff with an animal head and an open fork
at the base, probably representing the animal's legs. Its origins
date from the First Dynasty, and it was known as the "Heqa,"
or the cane used by shepherds to control their animals.
Who
held the Was Scepter? :
It was held by gods, pharaohs, and priests, and the animal differed
from one to another, denoting their particular dominion. The staff
was made of wood or faience and sometimes gold or silver. It was
an emblem of authority and associated with wealth and happiness.
What
was the Was Scepter used for? :
Besides being used as an amulet, it was also a type of magical
fetish; it was believed to create a bond between the mortal world
and the Underworld. Some gods combined the Was Scepter with Ankh
and Djed pillar-like god Ptah, who was known as the Sculptor of
the earth. It was found in the tombs of the Pharaohs as it was
believed to protect the well-being of the deceased.
28. Tyet (Knot of Isis) :

Tyet
Knot of Isis
What is the Tyet, and what does it look like? :
Tyet/Tjet is a famous ancient Egyptian symbol known as the Knot
of Isis or the blood of Isis or sometimes as Isis girdle. It is
very similar to the Ankh in shape but with arms bent downwards.
The Tyet dates back to the predynastic period; it was mainly used
with the Djed.
During the 3rd Dynasty of the Old Kingdom, Tyet became a popular
decorative symbol. In the New Kingdom, when Isis's cult was at
its peak, Tyet was associated with the Djed, representing Osiris,
Isis's husband.
What was the Tyet used for? :
The Tyet was a funerary amulet made of red stone or glass; it
was thought to bind magic as well; it was mentioned in the book
of the Dead that it should be buried with the mummy.
According to ancient texts, this amulet will keep the deceased
person strong and will protect him from whoever can harm him.
When it is paired with the Ankh, it offers protection from Isis
and Osiris, as it is believed it is an Egyptian symbol of protection.
What
does the Tyet symbolize? :
The Tyet was a symbol of eternal life and resurrection; the origin
of Tyet is not certain but is linked to blood, Power, and regeneration.
Anyway, it represents Isis in her role as a universal mother so
that it might act as an Egyptian symbol of family.
29. Shen :

Shen
What is the shape of the Shen, and what does it represent? :
The Shen has the shape of a circle with a perpendicular line in
its bottom. It represents a stylized loop of rope with ends tied
together. In hieroglyphic writing, it represents the word "Shenou,"
which means encircle.
What does the Shen symbolize? :
As the circle has no-end, the Shen ring symbolizes infinity &
Eternity. When it is represented by an enclosing sun disk, it
symbolizes the Eternity of life, as the Sun was the meaning of
life in ancient Egypt. When the Shen is gripped by deities, it
means protection.
What
was the Shen used for? :
Starting the Old Kingdom, Shen was primarily associated with Horus
the falcon and Nekhbet, the vulture who held Shen above the King's
head to protect him. The most prominent god related to the Shen
was "Huh," who represents infinity & Eternity.
During
the Middle Kingdom, Shen became very popular in jewelry and as
an amulet that Kings, Nobles, and Priests wore.
Starting in the New Kingdom, Shen became more popular; it was
presented in tombs and sarcophagi as a protection symbol. Starting
the 26th Dynasty and onwards, Shen was used by common people.
Who
used the Shen? :
The Cartouche is the elongated form of the Shen ring that also
symbolizes infinity used only by elites like Pharaohs, Princes,
Nobles, and Priests.
Source
:
https://www.tripidaysegytours.com/
wikipedia-egypt/popular-ancient-egyptian-
hieroglyphic-symbols-and-meanings