| MATSYA Matsya Kingdom was one of the sixteen Mahajanpads (great kingdoms). The kingdom was established by an Indo-Aryan tribe of Vedic India.
Location :
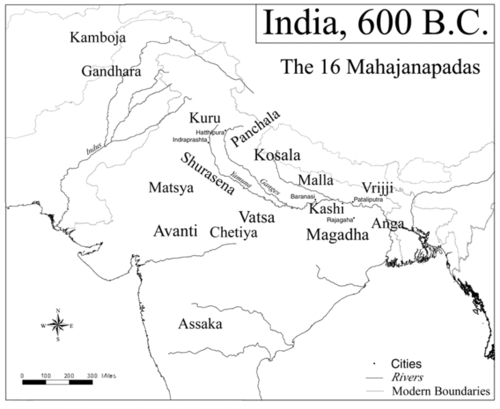
Ancient Indian Kingdoms in 600 BC By the late Vedic period, they ruled a kingdom located south of the Kurus, and west of the Yamuna river which separated it from the kingdom of the Panchals. It roughly corresponded to the former state of Jaipur in Rajasthan, and included the whole of Hindaun, Alwar with portions of Bharatpur.
Jat
clans :
History
:
In the early 6th century BCE, Matsya was one of the sixteen Mahajanpads (great kingdoms) mentioned in the Buddhist text Anguttara Nikaya, but its power had greatly dwindled and it was of little political importance by the time of Buddha. The Mahabharata (V.74.16) refers to a King Sahaj, who ruled over both the Chedis and the Matsyas, which implies that Matsya once formed a part of the Chedi Kingdom.
Other than the Matsya kingdom to the south of Kuru Kingdom, which falls in the Hindaun and Alwar, Bharatpur districts of Rajasthan, the epic refers to as many as six other Matsya kingdoms. Upaplavya was a notable city of the kingdom. On the 13th year of Pandava's exile, pandavas and Draupadi stay in matsya kingdom of King Virat.
Adhiraj :
Vijayendra Kumar Mathur has written ... Adhiraj ( AS , p.19): According to Mahabharat Sabha Parv [31,3] Sahadev defeated King Dantavakra of this country in the context of his Digvijay Yatra. - ‘Adhirajadhipam Chaiv Dantavakram Mahabalam, Jigay Kardan Jeev Kritwa Rajeya Nyaveyayat’. The mention of Adhiraj after Matsya indicates that this country must have been close to Matsya (the latter state of Jaipur). But Mr. no. La Dey is of the opinion that this was a later state of Rewa.
Matsya
district: Dalip Singh Ahlawat :
Matsya district was located on the land of Bharatpur, Alwar, Jaipur. Its capital was Virat or Vairat Nagar, which is still located 40 miles north of Jaipur. The king here was aged during the Mahabharata war. He gave 2000 elephants as gift to Yudhishthir's in his Rajasuya Yagna (Mahabharat sabha Parv, 52nd chapter; Verse 26th). This Virat king, despite growing old, fought in the Mahabharat war towards the Pandavs (Mahabharat Bhishma Parv 52nd chapter). This great King was a very brave warrior. In the name of this, a chapter of Mahabharat 'Virat Parv' is famous.
The queen of this great king, Sudeshn, was the sister of Keechak. At Matsya Desh Pandavs came for their Agyatvaas with Draupadi. Uttara, the daughter of the same king, was married to Arjunputra Abhimanyu. The son of both of them, Parikshit succeeded the Hastinapur state. King Virat's brother was Shataniq. Virat had two sons named Uttar and Shwet. In the Mahabharata war, Madraraj Shalya killed the Uttar and Bhishma killed the Shwet. Matsya Janpad was also one of the 16 Mahajanapadas of the Buddhist period. The symbol of the flag of this republic was fish.
On 15 August 1947, when India became independent, the Government of India formed the 'Matsya Union' by combining Alwar, Bharatpur, Dholpur and Karauli out of the princely states of Rajputana and forming the ' Rajasthan ' by merging the remaining princely states . In June 1949, the four princely states of Matsya Union were also merged in Rajasthan.
The power of the Matsyavansh (Mathur) is found in the Jats. On behalf of the state of Bharatpur, the Matsyavajas Jat Dheeraj Mathur and Nath Mathur were appointed to conduct the court by making the ruler of five villages named Karal, Pansali, Punth Khurd, Kiradi, Hastasar near Delhi. The ruins of this office are still lying in Karala. Settled in Kakan village (near Gohan) from this village itself. Additionally fish Mtsr or Macr Jat Bijnor Brawn and Umrpur inhabit villages. Rajasthan District Sikar in Khetri village belongs to the Jats of Matsya or Machhar gotra.
In
Mahabharat :
Source :
https://www.jatland.com/ |