| QUMIS
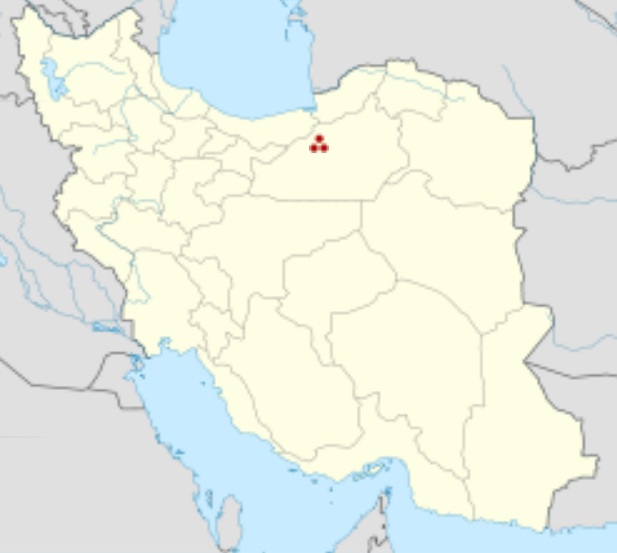
Šahr-e Qumis, Iran Alternative
name : Saddarvazeh, Hecatompylos
Qumis (Middle Persian: Komis), also known as Hecatompylos (in Persian: Saddarvazeh) was an ancient city which was the capital of the Arsacid dynasty by 200 BCE. The Greek name Hekatompylos means "one hundred gates" and the Persian term has the same meaning. The title was commonly used for cities which had more than the traditional four gates. It may be understood better as the "Many Gated". Most scholars locate it at Sahr -e Qumis, in the Qumis region in west Khurasan, Iran.
Alexander the Great stopped here in the summer of 330 BCE and it became part of the Seleucid Empire after his death. The Parni tribe took the city around 237 BCE and made it one of the first capitals of their Parthian Empire. It was mentioned as the royal city of the Parthians by a number of classical writers including Strabo, Pliny, and Ptolemy, although the Parthians seemed to have used a number of cities as their "capital" at different periods.
Qumis was destroyed by an earthquake in 856 AD, and it was probably abandoned afterwards. The site of this ancient city is now called Šahr-e Qumis, between Semnan and Damqan in the Semnan Province.
In 2011 plans for an "International Project of Tourism & Recreational City" were published, using the name of Hecatompylos. The project envisions using an area of 250 hectares (620 acres) close to the city of Damghan, which would place the resort at about 30 km (19 mi) northeast of the historic site.
Source :
https://en.wikipedia.org/ |