| DAHAE
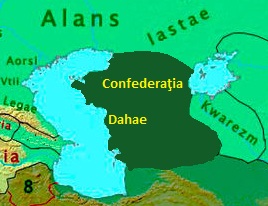
Dahae Location
: Present-day west and northwest Turkmenistan, far southwest
Kazakhstan and far west Uzbekistan (most of the Ustyurt Plateau)
The Dahae, also known as the Daae, Dahas or Dahaeans (Latin: Dahae; Persian: Dahan; Ancient Greek: Dáoi, Dáai, Dai, Dasai; Sanskrit: Das; Chinese: Dayi) were an Iranian people of ancient Central Asia. A confederation of three tribes – the Parni, Xanthii and Pissuri – the Dahae lived in an area now comprising much of modern Turkmenistan. The area has consequently been known as Dahestan, Dahistan and Dihistan.
Relatively little is known about their way of life. For example, according to the Iranologist A. D. H. Bivar, the capital of "the ancient Dahae (if indeed they possessed one) is quite unknown."
The Dahae dissolved, apparently, some time before the beginning of the 1st millennium. One of the three tribes of the Dahae confederation, the Parni, emigrated to Parthia (present-day north-eastern Iran), where they founded the Arsacid dynasty (The Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD), also known as the Arsacid Empire).
Origins
:
Some scholars also maintain that there were etymological links between the Dahae and Dacians (Dacii), a people of ancient Eastern Europe. Both were nomadic Indo-European peoples who shared variant names such as Daoi. David Gordon White, an Indologist and historian of religion, has reiterated a point made by previous scholars – that the names of both peoples resemble the Proto-Indo-European root: *dhau meaning "strangle" and/or a euphemism for "wolf". (Similarly, the Massagetae, the northern neighbors of the Dahae, have been linked to the Getae, a people related to the Dacians.)
The country neighbouring the Dahae to the south, Verkana – often known by its Greek name, Hyrcania – has sometimes been conflated with Dahistan. Like Dahae and Dacia, Verkâna appears to have a root in an Indo-European word for "wolf", the Proto-Iranian: *vrka. The name of Sadrakart (later Zadracart), the capital of Verkâna, apparently has the same etymological roots, and may be synonymous with one of two modern cities in Iran: Sari or Gorgan. (The modern name Gorgan is also derived ultimately from the Proto-Iranian *vrka for "wolf" and is cognate with the New Persian gorgan (i.e. v > g).
History
:
It is possible that the Dahae were confused in secondary accounts with a contemporaneous, possibly related people from Balkh (Bactria), who were known in ancient China as Daxia (also Ta-Hsia, or Ta-Hia). Whereas the Dahae were known in Chinese sources as Dayi. Later historical accounts place the Dahae entirely on the south-eastern shores of the Caspian Sea.
The first reliable mention of the Dahae is considered to be the Daev inscription by Xerxes the Great of Persia (reigned 486–465 BCE). In a list in Old Persian of the peoples and provinces of the Achaemenid Empire, the Daev identifies the Daha as neighboring the Saka.
It is unclear whether the Dahae are also the *Daha or *Dånha (only attested in the feminine Dahi) mentioned by the Avestani Yasht (13.144), which may date from the 5th century BCE. Moreover, any etymological relationship would not be proof that both names refer to exactly the same people.
Dahae and Saka tribes are known to have fought at the Battle of Gaugamela (331 BCE), in which the armies of the Achaemenid Empire were defeated by Alexander the Great. After the Achaemenid dynasty collapsed the following year, Alexander recruited Dahae – famed as mounted archers – for the Greek invasion of India.
Some "Saka" coins from the Seleucid era (312–63 BCE) are sometimes attributed to the Dahae. By the 3rd century BCE, the Parni Dahae had risen to prominence under a chief named Ashk (c. 250 – c. 211 BCE; Persian: Arshak; Latin Arsaces). The Parni invaded Parthia, which had just previously declared independence from the Seleucids, deposed the reigning monarch, and Ashk crowned himself king (Arsaces I in classical sources). His successors are often referred to as the Arsacids; they would eventually assert military control over the entire Iranian plateau. By then, the Parni would be indistinguishable from the Parthians, and would also be called by that name.
During the 1st Century BCE, the Dahae were reported to have sent envoys to China. According to the Chinese historian Yu Taishan, a contemporary Chinese account (the Shijii) mentions separate envoys from Huanqian (Khwarezm), Dayi (the Dahae) and Suxie (Soghdia), among others.
In the 1st century BCE, Strabo (Geographika 11.8.1) also refers to the Dahae as a "Scythian" people, who were located in the vicinity of present-day Turkmenistan. However, while the terms Scythians and Saka are usually regarded as synonymous, that is not always the case with Strabo.
Source :
https://en.wikipedia.org/ |