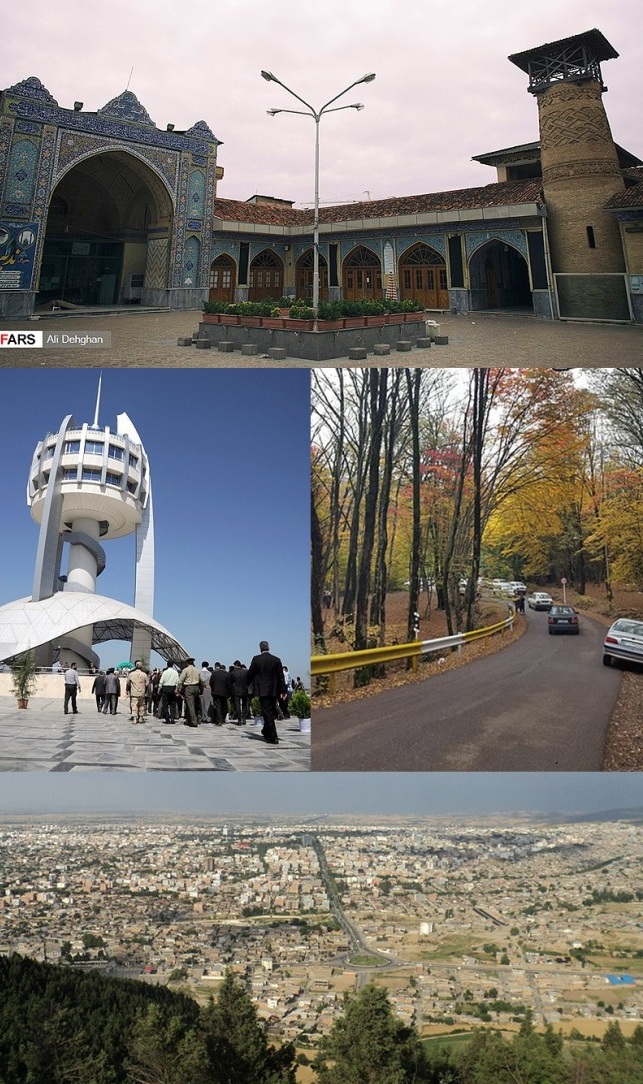
| GORGAN
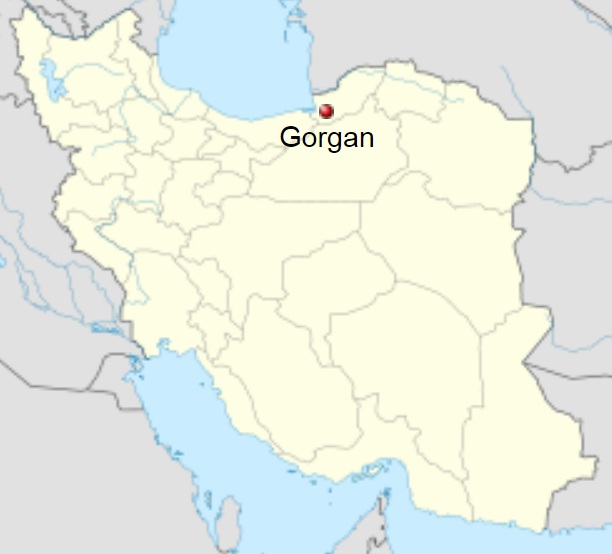
Gorgan, Esterabad Country
: Iran
Coordinates : 36°50'19 N 54°26'05 E
Gorgan (Also romanized as Gorgan, Gurgan, and Gurgan), formerly Astarabad also romanized as Astarabad, Asterabad, and Esterabad), is the capital city of Golestan Province, Iran. It lies approximately 400 km (250 mi) to the north east of Tehran, some 30 km (19 mi) away from the Caspian Sea. In the 2006 census; its population was 269,226, in 73,702 families.
History
:
Historic wall of Gorgan signs According to the Greek historian Arrian, Zadracarta was the largest city of Hyrcania and site of the "royal palace". The term means "the yellow city", and it was given to it from the great number of oranges, lemons, and other fruit trees which grew in the outskirts of that city.
Hyrcania became part of the Achaemenid Empire during the reign of Cyrus the Great (559–530 BC), its founder, or his successor Cambyses (530-522 BC).
The Great Wall of Gorgan, the second biggest defensive wall in the world, was built in the Parthian and Sassanian periods.
At the time of the Sassanids, "Gurgan" appeared as the name of a city, province capital, and province.
Gorgan maintained its independence as a Zoroastrian state even after Persia was conquered by the Muslim Arabs in the 8th century.
In 1210, the city was invaded and sacked by the army of Kingdom of Georgia under command of the brothers Mkhargrdzeli.
"Old Gorgan" was destroyed during the Mongol invasion in the 13th century, and the center of the region was moved to what was called "Astarabad", which is currently called "Gorgan".
Gorgan with its surrounding regions was sometimes considered as part of the Parthia (the Greater Khorasan) or the Tabaristan regions. Astarabad was an important political and religious city during the Qajar dynasty.
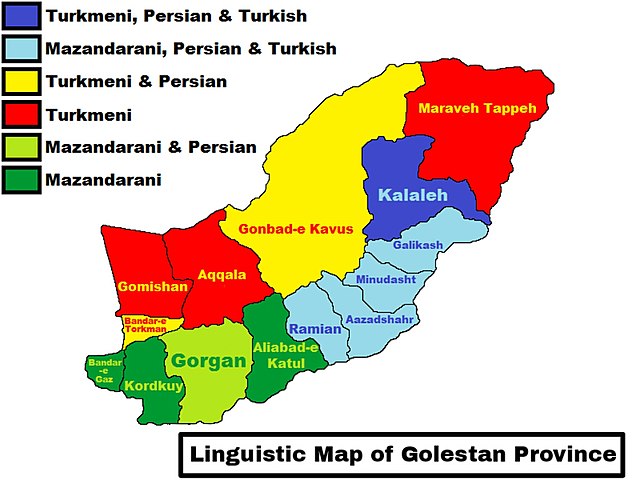
Linguistic Map of Golestan province
Geography and climate :
Some 150 km (93 mi) east of Gorgan is the Golestan National Park, home to a large portion of the fauna of Iran.
Gorgan has a mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: Csa). In general, Golestan has a moderate and humid climate known as "the moderate Caspian climate." The effective factors behind such a climate are: Alborz mountain range, direction of the mountains, height of the area, neighborhood to the sea, vegetation surface, local winds, altitude and weather fronts. As a result of the above factors, three different climates exist in the region: plain moderate, mountainous, and semi-arid. Gorgan valley has a semi-arid climate. The average annual temperature is 17.7 °C (63.9 °F) and the annual rainfall is 601 millimetres (23.7 in).
Historical figures :
Bust of Fakhruddin As'ad Gurgani
Picture showing Mirza Mehdi Khan Astarabadi in pink clothes and Nader Shah Afshar on horseback •
House of Karen,
an aristocratic feudal family first attested in the Arsacid era,
belonged to the region of Hyrcania.
Contemporary figures :
Mohammad Reza Lotfi •
Mohammad Reza
Lotfi, Traditional Persian musician
Education :
Mirdamad Cultural Institute (MCI) •
Golestan University
Currently the main football team of Gorgan is Etka Gorgan F.C., which competes in the Azadegan League.
Sister
cities :
Source :
https://en.wikipedia.org/ |