| INDO - IRANIAN LANGUAGES
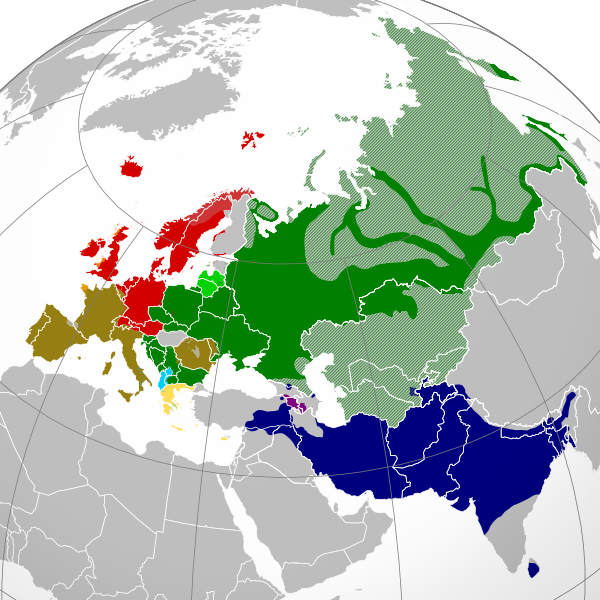
The approximate present-day distribution of the Indo-European branches of Eurasia
Geographic
distribution : South, Central, Western Asia, South East
Europe and the Caucasus / Total speakers = approximately 1.5 billion
in 15 countries
The Indo-Iranian languages (Indo-Iranic languages), or Aryan languages constitute the largest and south-eastern most extant branch of the Indo-European language family. They have more than 1.5 billion speakers, stretching from Europe (Romani), Turkey (Kurdish and Zaza–Gorani) and the Caucasus (Ossetian) eastward to Xinjiang (Sarikoli) and Assam (Assamese), and south to Sri Lanka (Sinhala) and the Maldives (Maldivian), as well as branching out to Oceania for Fiji Hindi. Furthermore, there are large diaspora communities of Indo-Iranian speakers in northwestern Europe (the United Kingdom), North America (United States and Canada), and Australia.
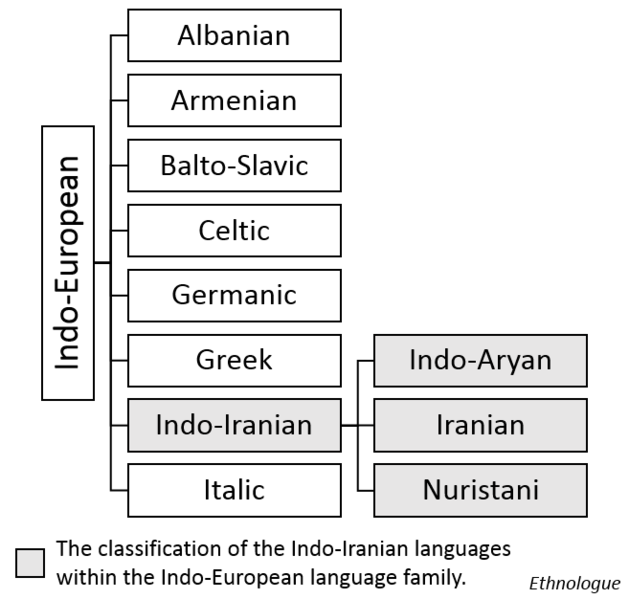
The common ancestor of all of the languages in this family is called Proto-Indo-Iranian—also known as Common Aryan—which was spoken in approximately the late 3rd millennium BC. The three branches of the modern Indo-Iranian languages are Indo-Aryan, Iranian, and Nuristani. A fourth independent branch, Dardic, was previously posited, but recent scholarship in general places Dardic languages as archaic members of the Indo-Aryan branch.
Languages :
Chart classifying Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European language family
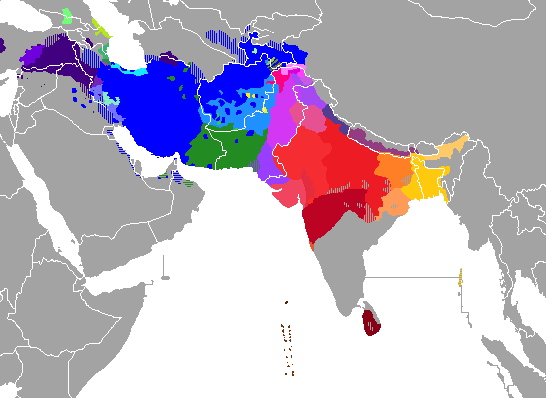
Distribution of the Indo-Iranian languages The Indo-Iranian languages consist of three groups :
•
Indo-Aryan languages
History
:
The oldest attested Indo-Iranian languages are Vedic Sanskrit, Older and Younger Avestan and Old Persian (ancient Iranian languages). A few words from another Indo-Aryan language are attested in documents from the ancient Mitanni and Hittite kingdoms in the Near East.
Within the Indo-European family, Indo-Iranian belongs to the Satem group. Various proposals have been made that link the Indo-Iranian languages with other subgroups of Indo-European (like Graeco-Aryan, which posits a close relationship with Greek and Armenian), but these remain without wider acceptance.
Source :
https://en.wikipedia.org/ |