| SAURASHTRA
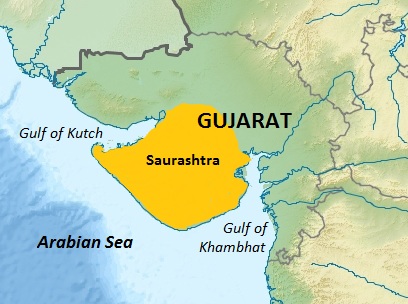
Saurashtra region within Gujarat, India
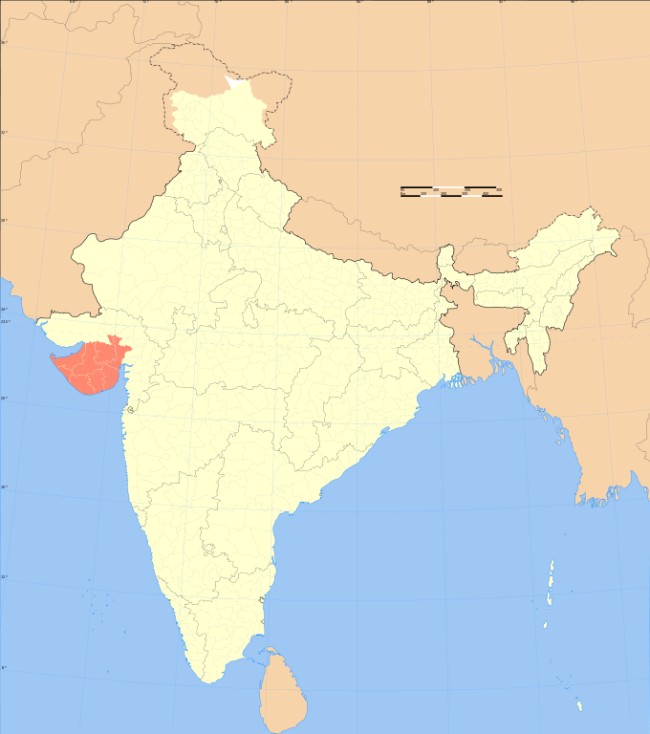
Location of Saurashtra in India Coordinates
: 22.3000° N 70.7833° E
Language : Gujarati
Large cities : Rajkot, Jamnagar, Bhavnagar, Morbi, Gir tourism (A home of Asiatic Lion) Junagadh, Porbandar, Veraval and Surendranagar.
Saurashtra and some part of it also known as Sorath or Kathiawar, is a peninsular region of Gujarat, India, located on the Arabian Sea coast. It covers about a third of Gujarat state, notably 11 districts of Gujarat, including Rajkot District. It was formerly a state of India before it merged with Bombay state. In 1961 it separated from Bombay and joined Gujarat.
Location
:
The peninsula is sometimes referred to as Kathiawar after the Kathi Darbar, which once ruled most of the region. However, Saurashtra is not entirely synonymous with Kathiawar, since a small portion of the historical Saurashtra region extends beyond the Kathiawar peninsula. Sorath forms the southern portion of the peninsula.
Districts
:
•
Devbhoomi Dwarka
History
:
— Periplus, Chap. 41
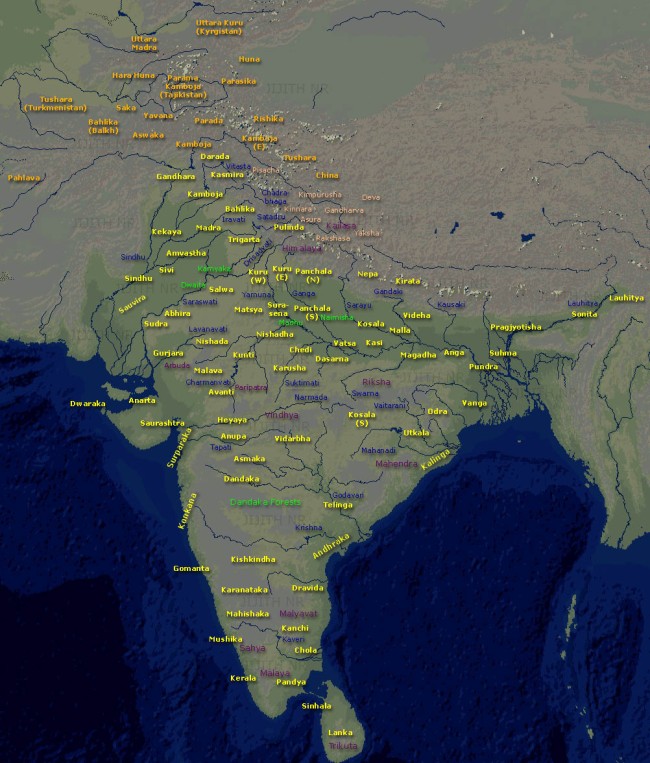
Map of ancient Indian kingdoms In earliest foreign mention, Egyptian mathematician, geographer, astrologer Claudius Ptolemy and Greek manuscript Periplus both call this region "Surastrene"
Saurashtra and its Prakrit name Sorath, literally means "good country". The name finds mentions in the Junagadh Rock inscription dating 150 CE, attributed to Rudradaman I. Prior to this, during the rule of Ashok (268–232 BCE), the region was under Yavan Tushasp, and governed by Pushyagupta during Chandragupt Maurya's reign (322BC – 298 BC). From the 8th to 11th century, Brahmin merchants from Saurashtra region started migrating towards Southern India due to the frequent Muslim invasions, these merchants upon the invitation of Chola, Pandya, Vijayanagar, Nayak and Thanjavur Maratha Kings set up mercantile silk-weaving guilds throughout Southern India and were involved in the trade of silk clothes and diamonds to the royal families of ancient South India, as the silk became the attire of royal families after the period of Gupta dynasty.
These Brahmins who trace their ancestry to the historical region of Saurashtra are now known as the Saurashtra people. Several historians believe that it was Saurashtrian textile merchants who introduced idly to South India during the 10th and 12th centuries. There are even claims that a mix of rice and urad dal ground together and later steamed to form cakes had its origins in Gujarat. This was called Iddada.
Gir
:
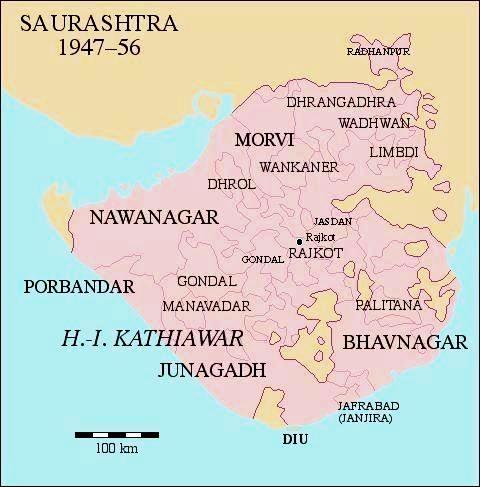
Saurashtra State :
After India's independence in 1947, 217 princely states of Kathiawar, including the former Junagadh State, were merged to form the state of Saurashtra on 15 February 1948. Initially, it was named United State of Kathiawar, which was renamed to Saurashtra State in November 1948. The exercise took up a lot of Shri Vallabhbhai Patel's time to convince the local princes and petty subas (totalling 222 in Saurashtra alone). However, Maharaja Krishnakumar Sinhji of Bhavnagar State readily extended to offer his large and royal empire of Bhavnagar / Gohilwar to Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, and Bhavnagar became the first in the country to be merged into the union of India.
The capital of Saurashtra was Rajkot. Uchharangray Navalshankar Dhebar, who later went on to become President of the Indian National Congress between 1955 and 1959, became Saurashtra's first Chief Minister. He was succeeded by Rasiklal Umedchand Parikh on 19 December 1954.
On 1 November 1956, Saurashtra was merged into Bombay state. In 1960 Bombay state was divided along linguistic lines into the new states of Gujarat and Maharashtra. The territory of Saurashtra, including Junagadh and all of Sorath, became part of the state of Gujarat.[citation needed]
Language
:
Postage
stamps :
The issue of 1877 was the first to include Latin letters; the circular design included the inscription "SORUTH POSTAGE" at the top, and "ONE ANNA OF A RUPEE" (or "FOUR ANNAS...") at the bottom. Some of these were surcharged in 1913–14, followed by redesigned stamps in 1914.
A set of eight stamps in 1929 included pictures of Junagadh, the Gir lion, and the Kathi horse in addition to the nawab. In 1937 the one anna value was reissued reading "POSTAGE AND REVENUE".
The Indian province of Saurashtra did not design any of its own stamps, but before adopting the stamps of India, Saurashtra issued a court fee stamp overprinted for postal use, then created more one anna stamps by surcharging three stamps of the 1929 issue.
Natural resources :
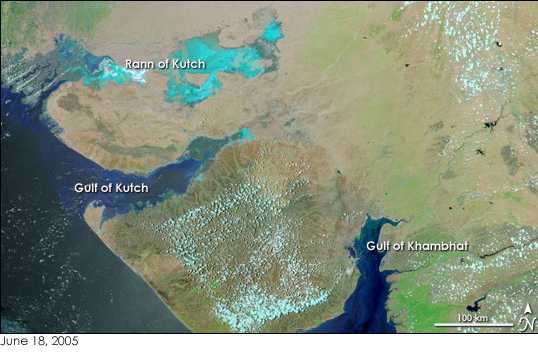
Saurashtra between Gulf of Kutch and Gulf of Khambat. Image NASA Earth Observatory Saurashtra has been a flourishing region and rich in natural resources since ancient times, while having gone through several droughts especially during the 20th century. Water resources and its related dynamics have influenced the region and its agro-economy to a certain extent. It is found that water was easily available in the region 10 to 15 years ago. Ashvin A. Shah, a US-based engineering consultant who conducted a survey in 1998 on water availability in the region, says, "The presence of 700,000 dugwells in Saurashtra region indicates the presence of extensive groundwater aquifers throughout the region. This means there is one well for fewer than 20 people or one well every 300 metres".
Amri Saurashtra went through severe droughts over the years to the extent that people could no longer grow crops, nor did they have drinking water available. There has been in recent times a campaign to take up rain water harvesting.
Significantly, the Check dam campaign from the late 1990s brought almost a drastic change resulting in raising water tables in Saurashtra. However, in 2019, the region was hit with a severe drought, affecting 20 districts in Gujarat, and water had to be brought in by tanker from the Sardar Sarovar Dam on the Narmada River.
Source :
hhttps://en.wikipedia.org/ |