| SHURSEN
Shursen and other Mahajanpads in the Post Vedic period Kingdom of Shursen : c. 700 BCE – c. 300 BCE
Capital : Mathura
Common
languages : Sanskrit
Kingdom of Shursen (or Soursen) (Sanskrit: Shursen, Shursena) was an ancient Indian region corresponding to the present-day Braj region in Uttar Pradesh, with Mathura as its capital city. According to the Buddhist text Anguttar Nikaya, Shursen was one of the solas (sixteen) Mahajanpads (powerful realms) in the 6th century BCE. Also, it is mentioned in the Hindu epic poem, the Ramayan. The ancient Greek writers (e.g., Megasthenes) refer to the Sourasenoi and its cities, Methora and Cleisobra.
Etymology
:
History :
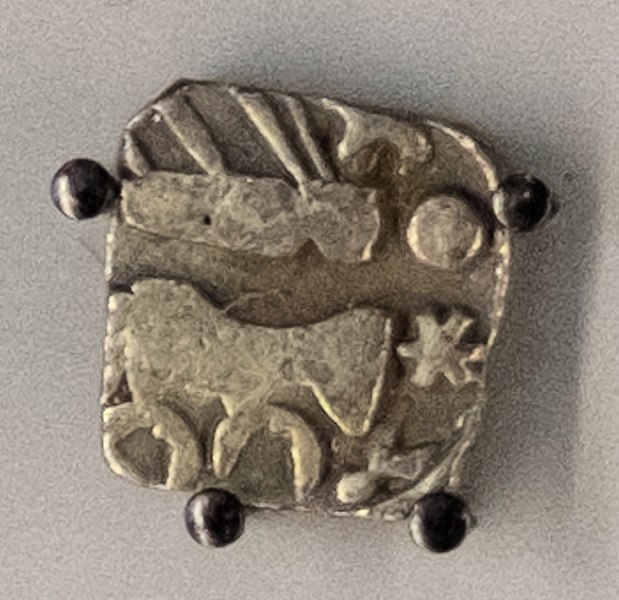
Shursen coin, 400 - 300 BCE The Mahabharat and the Purans refer to the rulers of the Mathura region as the Yadus or Yadavs, divided into a number of septs, which include the Vrishnis. The Buddhist texts refer to Avantiputta, the king of the Shursen in the time of Maha Kachchan, one of the chief disciples of Gautam Buddh, who spread Buddhism in the Mathura region.
Its capital, Mathura, was situated on the bank of the river Yamuna, presently a sacred place for the Hindus. The ancient Greek writers mention another city, named Cleisobora, in this region.
Archaeological excavations at Mathura show the gradual growth of a village into an important city. The earliest period belonged to the Painted Grey Ware culture (1100-500 BCE), followed by the Northern Black Polished Ware culture (700-200 BCE). Mathura derived its importance as a center of trade due to its location where the northern trade route of the Gangetic Plain met with the routes to Malwa (central India) and the west coast.
Source :
https://en.wikipedia.org/ |
.jpg)
