| HELMAND AND HALIL RUD
The Helmand culture (also Helmand civilization) is a Bronze Age culture that flourished mainly in the Helmand valley in the eastern Iran (Sistan and Baluchestan Province) and south Afghanistan (Helmand Province), predominantly in the third millennium BC.
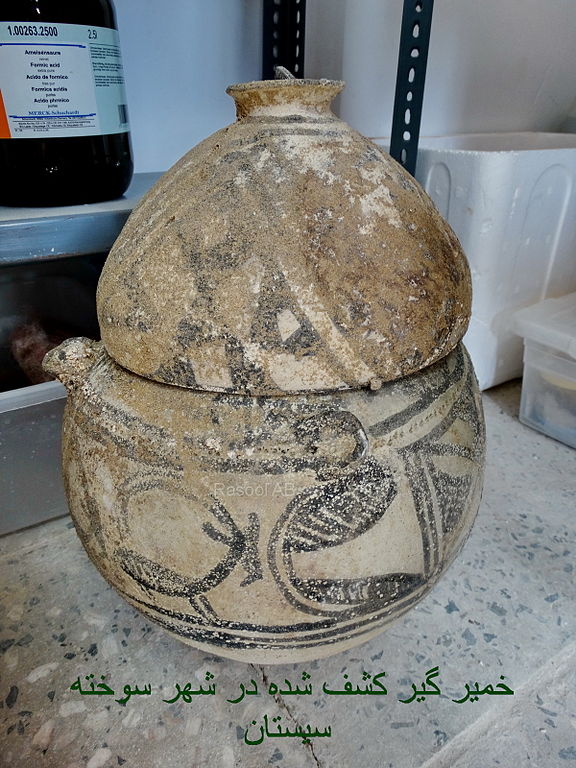
The people of the Helmand culture lived partly in cities with temples and palaces, providing evidence for a complex and advanced social structure. The main cities so far known are Shahr-e Sukhteh (in modern Iran) and Mundigak (Afghanistan). Research on the finds from both places showed that these cities shared the same culture. These are the earliest cities in this part of the world. It is possible that the Helmand culture formed once one ancient state.
The pottery of the Helmand civilization is colorfully painted with mainly geometrical patterns, plants and animals are also depicted. Bronze was known. In Shahr-e Sukhteh were found texts in Elamite language providing evidence with connections to the west of the Iran. There are also a few connections with the Indus Valley Civilisation, but it seems that the Helmand civilization was earlier and did not overlap chronological very much with the cities in the Indus valley.
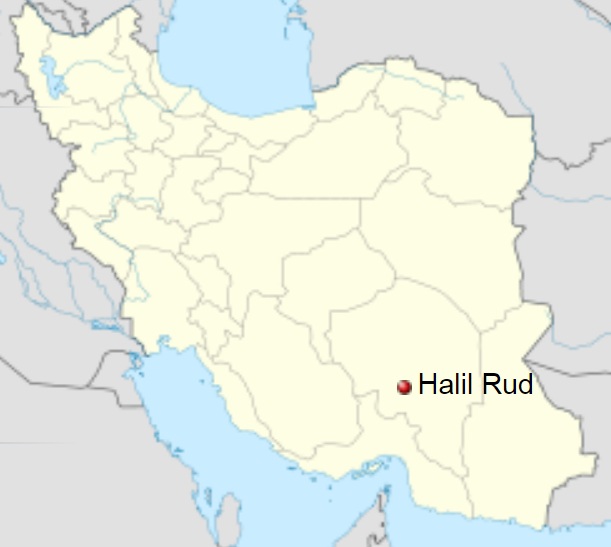
Halil Rud :
Country : Iran
Province : Kerman
County : Rabor
Bakhsh : Hanza
Rural District : Javaran
Coordinates : 29°04'52 N and 56°59'43 E
Halil Rud (also known as Deh-e Halil Rud) is a village in Javaran Rural District, Hanza District, Rabor County, Kerman Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 238, in 50 families.
Source :
https://en.wikipedia.org/
https://en.wikipedia.org/ |