| DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PERSIA AND IRAN
Map of Iran and Central Asia The names Iran and Persia are often used interchangeably to mean the same country. Iran is the legal name. Persia, was an ancient kingdom within Iran. Iran came to be known as Persia in the West thanks to classical Greek authors during whose time Persia was the dominant kingdom in Iran. To call all of Iran 'Persia', would be like calling all of Britain 'England'.
The name 'Persia' comes from 'Pers' which is in turn the European version of 'Pars' - an area that is today a province of Iran (see the map at the bottom of this page). 2,500 years ago, when the present provinces of Iran were kingdoms [at one time Iran (then Airan) consisted of 240 kingdoms*], Pars was known as Parsa, and the kings of Parsa established an empire that came to be known in the West as the Persian Empire - the largest empire the world have ever known to that point. In those days, Parsa was the dominant kingdom of all the Iranian or Aryan kingdoms.
[*Note: According to the Middle Persian (Pahlavi) Kârnâmak-i Ardeshir-i Pâpakân / Kârnâmag-î Ardashîr-î Babagân, Book of the Deeds of Ardashir son of Babak / Babag, the Book of Deeds, "there were in the territory of Iran two hundred and forty princes" at the beginning of Parthian rule of Iran/Airan. The dominant kingdom of Iran has at various times been Balkh (Bactria), Mada (Media), Parsa (Persia), Parthava (Parthia) and then Persia again. The king of the dominant kingdom was called king-of-kings (shah-en-shah in modern terms) - an emperor.]
Evolution of the Name Iran :
Over time, Airyana Vaeja became Airan-Vej, then Eran-Vej or Airan-Vej (the Parthians and Sassanians had a slightly different pronunciation), then Eran or Airan, and finally Iran.
Location of Ancient Iran :
For a more detailed discussion on the possible location of Airyana Vaeja, please see our page on the Location of the Aryan Homeland, Airyana Vaeja.
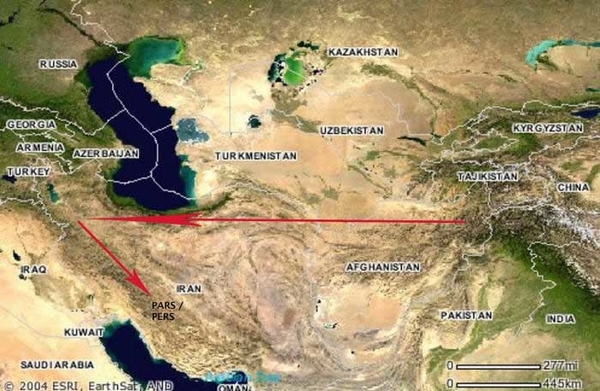
Map showing Iran and Central Asia and the possible movement of the Persian-Aryans culminating in the formation of Persia Growth
of Iran & Formation of Persia
Since the Vendidad's list of nations does not include two Aryan kingdoms, Parsa (Pars/Pers/Persia) or Mada (Media), we are left to conclude that these nations had not been formed - at least as autonomous kingdoms or nations in the fashion of the other sixteen lands - at the time the list was assembled. Even Iranian legends such as those contained in the poet Ferdowsi's epic, the Shahnameh or Book of Kings, do not mention Persia or Media during the early legendary phase. Instead, Pars/Persia is mentioned in Shahnameh later in history in connection with the invasion by Alexander. In the early Iranian history phase, the Shahnameh makes first mention of a greater Iranian nation, an empire, during the reign of King Feridoon.
While the Shahnameh does not mention Persia during the reign of King Feridoon, his sons married the daughters of the King of Yemen (we presume this is the same Yemen as the one in the south of the Arabian peninsula) thereby forming an alliance between ancient Iran and Yemen. Feridoon's Iranian Empire stretched from the borders of China to the borders of Europe (say up to Greece), and was large enough for it to be divided and administered by his three sons. Ferdowsi appears to locate Feridoon's capital as being in the southern Caspian coastal region, in or near Sari (in present-day Mazandaran, west of Gorgan, Golestan). Despite its lateral size, Feridoon's ancient Iranian Empire does not appear to have extended its western borders in width to include the later southwest land where Parsa would eventually be located, for we do not find mention in the Shahnameh of lands south of what is today Kurdistan and perhaps Lorestan (Narwan?).
During the reign of the subsequent Kayanian dynasty (Zarathushtra lived during the reign of Kayanian King Vishtasp) which assumed dominance over the Aryan nations, the Shahnameh no longer has the capital of Greater Iran located near Sari, but rather in Balkh (Bactria), in the north of Afghanistan today.
Extent of Iran. Aryana :
Aryana eventually extended from Central Turkey in the west to the Taklamakan Desert in the east, from the mid-Caspian region in the north (the northern borders of the various countries with names ending in -stan) to the Persian Gulf and the western Indus delta in the south. As we had mentioned earlier, this region at one time included 240 kingdoms.
The borders of present-day Iran are a greatly contracted version of Aryana engineered mainly by the British and the Russians who successively carved of portions in their expansions of the British and Russian Empires. The British and Russian engineering of Iran's borders followed in the footsteps of the earlier Arab invasion and then Ottoman expansion both of which effectively removed the Tigris-Euphrates basin (Eastern Iraq today) from the Greater Iranian domain.
Formation of Persia :
Chishpish / Teispes (675-640 BCE) an early king of the Achaemenid dynasty of Persian kings - the first recorded Persian dynasty - as well as subsequent Achaemenian kings including Cyrus, referred to themselves as kings of Anshan. Anshan (Anzan) is said to have been a former Elamite city and state to the southeast of Elam and possibly bordering Pars where the Parsa/Parsi established their eventual homeland. If the connection between Parsua, Parsumash / Parsamash or Parsuash and Parsa/Pars/Pers/Persia is correct, then we do have what appears to be a south-eastern movement by the Persians some thousand kilometres from Urmia to Pars. If the Persians were indeed migrants, then where was their original home?.
Greek historian Herodotus (c. 485-420 BCE) in his Histories notes 7.62: "The Medes had exactly the same equipment as the Persians; and indeed the dress common to both is not so much Persian as Median. They had for commander Tigranes, of the lineage of the Achaemenids. These (the Medes & Persians) were called anciently by all people Aryans." Herodotus (485 - 420 BCE) says that the Median (and Persian) association as Aryans was already 'ancient' in relation to the mid-first millennium BCE, the time when he lived. The Persian (Parsa/Parsi) kings themselves declare their Arya (Aryan) lineage in their inscriptions. Today, in the north-western Afghan province of Herat, anciently called Aria (Arya), we find a people called the Parsiban (Parsi-ban could be a derivative of the older Parsa-van, meaning 'people of the Parsa/Parsi'. We are inclined to draw some connections between to two Parsis rather than ascribing this homonym to coincidence.
The Persian migration theory is not universally accepted. There are those who believe that the Persians were autochthonous or aboriginal to the region of Pars. If so, the lack of mention of Parsa/Pars in both the Vendidad list of nations and the early Shahnameh, and well as the predominance of pre-Parsa Elamite artefacts in the Pars area beg a reasonable explanation. The Parsua, Parsumash / Parsamash or Parsuash will also need to be re-identified.
Persian Rise to Dominance Over the Aryan Nations :
Cyrus then added surrounding non-Aryan countries to his Persian Empire - especially countries to the west of Persia and Media. In this manner, the Persian Empire grew to include lands that extended from the lower Indus valley in the southeast corner, to Central Asia in the northeast, to Babylon in the centre, Egypt and Ethiopia in the southwest, and Asiatic Greece in the northwest. By the time Cyrus had finished putting together the Persian Empire, it had become the largest empire the world had ever known to that point in history.
The Achaemenid Persian Empire came to a close at the hands of Alexander of Macedonia in 330 BCE. A general of Alexander's established the Seleucid Empire which ruled over the previous Persian Empire until the Seleucids were overthrown by the Aryan Parthians in 248 BCE. Dominance of the Iranian (Aryan) nations now passed on the the Parthians. Parthia was a kingdom located in the northeast of present day Iran (around today's Khorasan province). Parthian rule lasted until it was replaced by the Persian Sassanian dynasty in 226 CE. The Persians thus resumed dominance of Iran until they were yet again overthrown - this time by the Arabs. The old noble and great Iran thus died, perhaps forever. It continues to live, however, in many hearts.
First Use of the Name Iran :
We find the first use of the modern derivative of Aryana, Eran or Airan, in the rock inscriptions of the Persian Sassanian kings (who ruled from 226 to 651 ACE). These inscription can still be seen at Naqsh-e-Rustam, a historical site containing royal tombs, and some 12 km northwest of the ancient Persian capital city of Persepolis in Pars. In the inscriptions, King Ardeshir I (226-241 ACE) is referred to as king of kings of Eran. This was when the Persian Sassanian dynasty displaced the Parthian Ashkanian kings as the Aryan king-of-kings.
It was usual that when such a coup took place, for the various Aryan nations or kingdoms to assert independence from central authority and for the rebellion to be met with a strong response from the coup leader to consolidate power.
Ardeshir's son and successor King Shahpur (241-272 ACE) moved to consolidate dominance as king of kings over the other Aryan / kingdoms nations and to rebuild the Aryan Empire to its former extent under the Achaemenid Persians. His inscriptions refer to Eran and An-eran i.e. Aryan and non-Aryan kingdoms, the latter being nations such as Syria and Cilicia. The words Eran-shahr meaning 'place of the Aryans' was also used by the Sassanians in describing the Iranian nation. These words would evolve to Iran-shahr.
Continued Western Use of the name Persia for Iran :
Iranian Capital Moves to Tehran :
Pars and Fars :
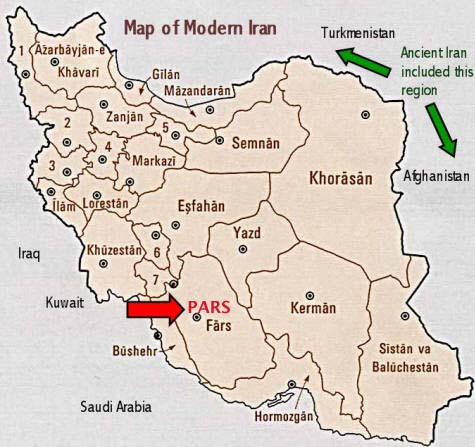
Map of Modern Iran showing Pars / Fars In the 7th century CE, the Arabs conquered Iran and converted the mainly Zoroastrian population to Islam. The Arabs pronounced the name Pars as Fars (because Arabic does not have the 'p' sound) and this version of the name has persisted even after the departure of the Arabs. The more authentic name is Pars and not Fars.
In the map of modern Iran at the right, the province of Fars (old Pars or Parsa) can be seen in the bottom-centre or southern Iran.
Parsi and Farsi :
While the words Parsi and Farsi are synonymous, today the Arabized name Farsi is used to mean the Persian language. The initial wave of Zoroastrian refugees who fled to India after the Arab invasion of Iran, now use of the authentic name 'Parsi' as their ethnic group name.
Source :
http://www.heritageinstitute.com/ |